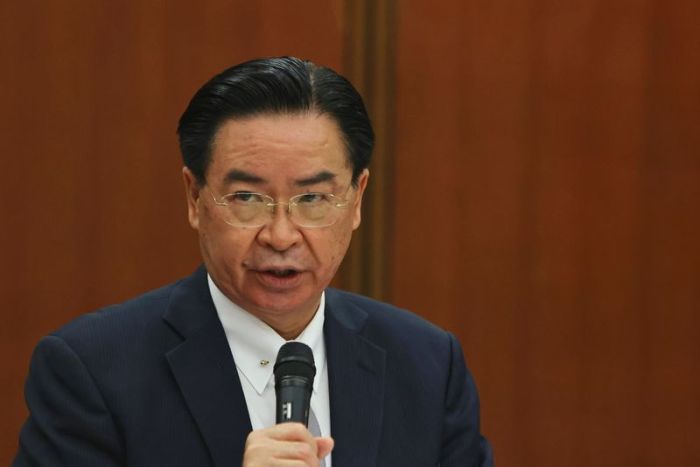
SAN FRANCISCO (Reuters) – Epic Games faces an uphill legal battle against Apple Inc in an antitrust trial starting Monday, and a defeat for the maker of “Fortnite” could make it harder for U.S. government regulators to pursue a similar case against the iPhone maker, legal experts said.
But win or lose at the trial, Epic, which has pursued an aggressive public relations campaign against Apple alongside its court pleadings, may have already accomplished a major goal: Drawing Apple squarely into the global debate over whether and how massive technology companies should be regulated.
Apple has mostly succeeded in staying out of the regulatory crosshairs by arguing that the iPhone is a niche product in a smartphone world dominated by Google’s Android operating system. But that argument has become harder to sustain with the number of iPhone users now exceeding 1 billion.
Epic alleges Apple has such a strong lock on those customers that the app store constitutes a distinct market for software developers over which Apple has monopoly power. Apple is abusing that power, Epic argues, by forcing developers to use Apple’s in-app payment systems – which charge commissions of up to 30% – and to submit to app-review guidelines the gaming company says discriminate against products that compete with Apple’s own.
“It’s not a super-strong suit – I don’t think they are likely to win,” said Rebecca Haw Allensworth, a law professor at Vanderbilt Law School. “But it has already achieved a lot of its purpose, which is drawing attention to some of Apple’s practices that many developers see as abusive.”
UPHILL BATTLE
Epic’s arguments draw on major antitrust cases against Microsoft, Eastman Kodak and American Express, but apply those precedents in new ways that have not been tested in U.S. courts, legal experts said.
For example, in arguing that iPhones are a software market unto themselves, Epic relies partly on a 1992 U.S. Supreme Court decision that rejected efforts by Kodak to force owners of its copying machines to use Kodak repair services.
Spencer Waller, a competition law professor at the Loyola University Chicago School of Law, said the Kodak decision has had mixed success in subsequent cases.
“Plaintiffs are often unsuccessful because courts read Kodak narrowly at times,” Waller said.
Epic also faces hurdles in its contention that Apple’s in-app payment commissions are too high at 30% and could be as much as 10 times lower if market forces prevailed. American courts have been reluctant to dive into setting specific rates, in large part because unlike Europe, the prevailing interpretation of U.S. antitrust law does not consider a dominant firm charging high prices to be anticompetitive in itself.
Apple argues that whatever dominant position it may have in mobile software is an outgrowth of its creation of both the iPhone and a curated App Store that makes consumer comfortable.
“If you obtained a monopoly legitimately, you’re allowed to charge high prices,” said Randal Picker, a professor at the University of Chicago Law School.
Regardless of who wins at the trial expected to last three weeks before Judge Yvonne Gonzalez Rogers in Oakland, California, the case is all-but-certain to be appealed to the U.S. Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals, which last year reinforced the notion that dominant firms can charge high prices in a case involving Qualcomm Inc.
“Anticompetitive behavior is illegal under federal antitrust law. Hypercompetitive behavior is not,” Circuit Judge Consuelo Callahan wrote in the court’s opinion.
A federal antitrust official, speaking anonymously because the official was not authorized to speak to the media, said that an Epic loss would dim the chances of the government pursuing a similar lawsuit against Apple.
BREWING ANTITRUST DEBATE
Epic’s suit has ramped up pressure on Apple in the court of public opinion at a time when the iPhone maker’s business practices are facing fresh scrutiny around the world.
The U.S. Department of Justice https://reut.rs/3vAq5sD is probing the company’s practices, Reuters has reported, and regulators in the United Kingdom and Australia have opened probes or called for regulation.
European Union regulators last week accused Apple of distorting competition in the music streaming market, siding with Spotify Technology in the zone’s first major anti-competition charge against Apple.
Epic advertisements decrying Apple for taking such a big cut of revenue are landing aside those headlines.
“The public can understand these issues, and in many ways understand them better than these judges who have never played a game in their life,” said Thomas Horton, a professor at the University of South Dakota School of Law.
The biggest threat to Apple’s App Store is not lawsuits, but rather new laws regulating digital platforms, said Joel Mitnick, a partner at Cadwalader, Wickersham & Taft and a former U.S. Federal Trade Commission trial lawyer.
European lawmakers have already proposed legislation that could require Apple to allow developers to use their own payment systems, and consensus for new regulations is building in the United States as well.
Mitnick noted that concern about the power of big tech companies was bipartisan.
“If it were me, I would be looking at ways in which I could influence what might be inevitable changes to the rules under which (Apple) are going to operate,” he said.
(Reporting by Stephen Nellis in San Francisco; Additional reporting by Paresh Dave in Oakland, California; Editing by Jonathan Weber and Lisa Shumaker)