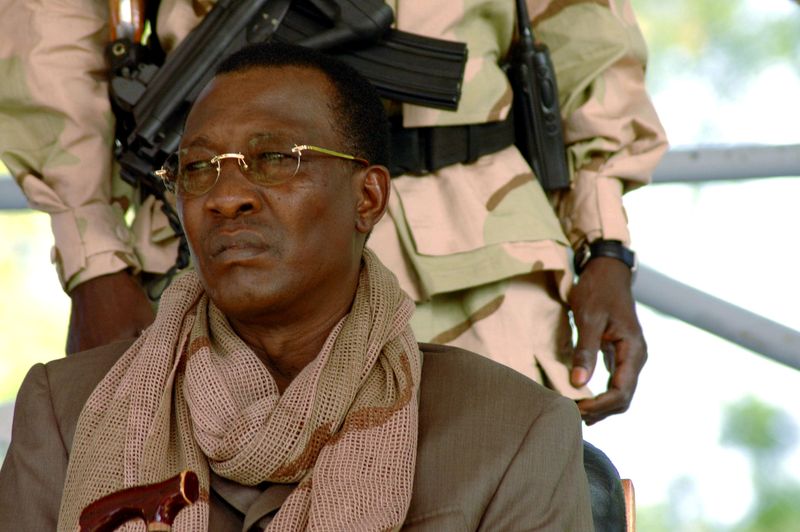
N’DJAMENA (Reuters) -Chad’s president, Idriss Deby, who ruled his country for more than 30 years and was an important Western ally in the fight against Islamist militants in Africa, was killed on Monday in a battle against rebels in the north, authorities said.
His son, Mahamat Idriss Deby, was named interim president by a transitional council of military officers, army spokesman Azem Bermendoa Agouna said on state television on Tuesday.
Deby, 68, took power in a rebellion in 1990 and was one of Africa’s longest-ruling leaders, surviving numerous coup attempts and rebellions. His death, the exact cause of which was unclear, could deepen Chad’s problems, as well as those of its allies.
On the domestic front, the military is divided and the opposition bridling against years of repressive rule.
Internationally, France and the United States will be hoping their counterterrorism efforts are not now pushed off course.
France said it had lost a “brave friend” and Chad “a great soldier”. The White House offered “sincere condolences” to the people of Chad and supported “a peaceful transition of power in accordance with the Chadian constitution.”
Deby’s death was announced a day after he was declared winner of a presidential election that would have given him a sixth term in office. Most of the opposition boycotted the vote.
Deby, who often joined soldiers on the battlefront in his military fatigues, visited troops on the front line after rebels based across the northern frontier in Libya advanced hundreds of kilometres (miles) south toward the capital, N’Djamena.
“Marshal Idriss Deby Itno, as he did each time that the institutions of the republic were gravely threatened, took control of operations during the heroic combat led against the terrorists from Libya. He was wounded during the fighting and died once repatriated to N’Djamena,” Bermendoa said.
He did not comment on when Deby died, but funeral arrangements issued by the government said it was on Monday.
The government and National Assembly have been dissolved and a nationwide curfew imposed from 6 p.m. to 5 a.m.
The army wants to return power to a civilian government and hold free and democratic elections in 18 months, Djimadoum Tirayna, vice president of the Transitional Military Council, said in a statement on state television.
The Libya-based Front for Change and Concord in Chad (FACT) rebels rejected the transition plan and vowed to continue their offensive towards the capital.
“Chad is not a monarchy. There can be no dynastic devolution of power in our country,” the rebels, who were fighting to oust Deby, said in a statement.
Deby had pushed through a new constitution in 2018 that would have allowed him to stay in power until 2033. He said before the April 11 election: “I know in advance that I will win, as I have done for the last 30 years.”
He was dealing with mounting public discontent over his management of Chad’s oil wealth and crackdowns on opponents. In the election results, Deby claimed 79% of the vote.
Opposition politician Saleh Kebzabo, who finished second in a 2016 election and took part in the latest boycott, decried the military’s move to take power and called on it to agree to a national dialogue.
“They will be obliged because of the internal political pressure,” he told Reuters. “We represent an internal force that cannot be ignored, neither by the military nor by the rebels.”
People in N’Djamena feared that fighting could break out after the news of Deby’s death, a Reuters witness said, but the streets were quiet in the afternoon.
UNCERTAINTY
Western countries had counted on Deby as an ally in the fight against Islamist militants, including Boko Haram in the Lake Chad Basin and groups linked to al Qaeda and Islamic State in the Sahel.
France, the former colonial power, had based its Sahel counterterrorism operations in N’Djamena. Chad announced in February the deployment of 1,200 troops to complement 5,100 French soldiers in the area.
The French presidency affirmed its support for Chad’s stability and territorial integrity. In a statement, it said it hoped there would be a quick and peaceful return to civilian rule.
Nigerian President Muhammadu Buhari said Deby’s death would create a “big vacuum” in efforts to fight jihadists in the region.
His death could mean tremendous uncertainty for Chad, said Nathaniel Powell, author of a history of French military involvement in Chad.
“The swift announcement of the establishment of a military council and naming his son Mahamat as head of state, however, indicates regime continuity,” Powell told Reuters.
“This probably aims to counter any coup-making efforts from within the security establishment and to reassure Chad’s international partners.”
A regional diplomat said the naming of Deby’s son as interim president was problematic as the speaker of parliament should have taken power on his death.
“That in itself is a coup,” the diplomat said. “He has been grooming the son for some time.”
The latest rebel actions had already caused alarm in Washington and other Western capitals.
FACT fighters attacked a border post on election day, then advanced south through the vast country.
The Chadian military appeared to have slowed the rebels’ progress about 300 km (185 miles) from N’Djamena.
The rebels said they suffered losses on Saturday but that they were back on the move on Sunday and Monday.
Deby loved to visit troops on the front lines. He joined the army in the 1970s when Chad was engaged in a long civil war. He received military training in France and returned to Chad in 1978, throwing his support behind President Hissène Habré and eventually becoming commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
A dozen years later, he led a rebel army in a three-week offensive staged from neighbouring Sudan to topple Habre, who was accused of widespread human rights abuses.
(Reporting by Mahamat Ramadane; Additional reporting by Madjiasra Nako in N’Djamena, Aaron Ross in Dakar, David Lewis in Nairobi and Jonathan Landay and Susan Heavey in Washington; Editing by Angus MacSwan, Sonya Hepinstall and Peter Cooney)