NEW DELHI (Reuters) – India and China on Thursday began to pull back troops and battle tanks from a bitterly contested lake area high in the western Himalayas on Thursday in a breakthrough after a months-long standoff on the disputed border.
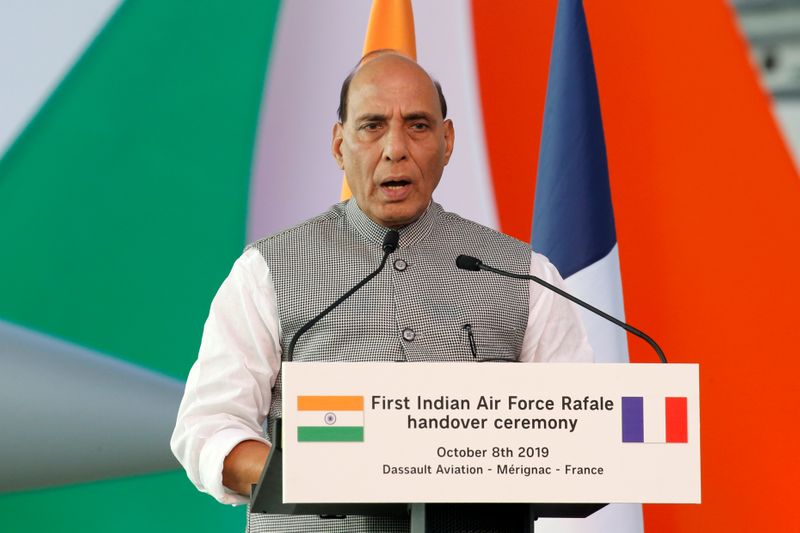
Indian Defence Minister Rajnath Singh told parliament the two sides had reached an agreement to withdraw from Pangong Tso, a glacial lake at 14,000 ft (4,270 metres), after several rounds of talks between military commanders and diplomats from the nuclear-armed neighbours.
“Our sustained talks with China have led to agreement on disengagement on the north and south banks of the Pangong lake,” he said.
China’s defence ministry announced on Wednesday that frontline troops from the two countries were pulling back from the shores of the lake on Wednesday.
The standoff began in April last year when India said Chinese troops had intruded deep into its side of the Line of Actual Control or the de facto border in the Ladakh area in the western Himalayas.
China said its troops were operating in its own area and accused Indian border guards of provocative actions.
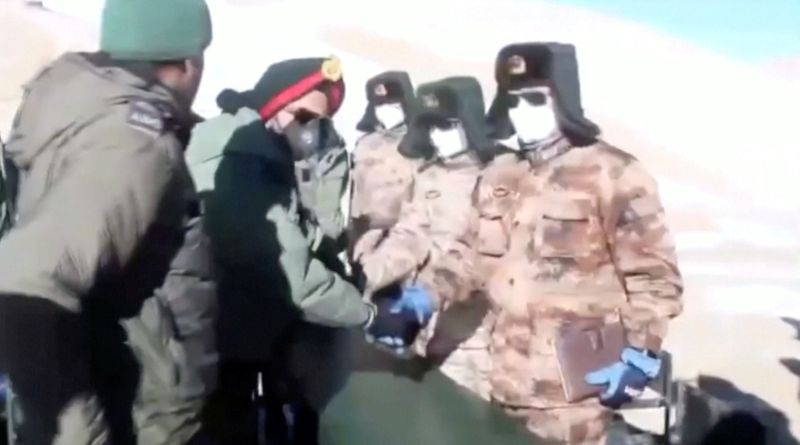
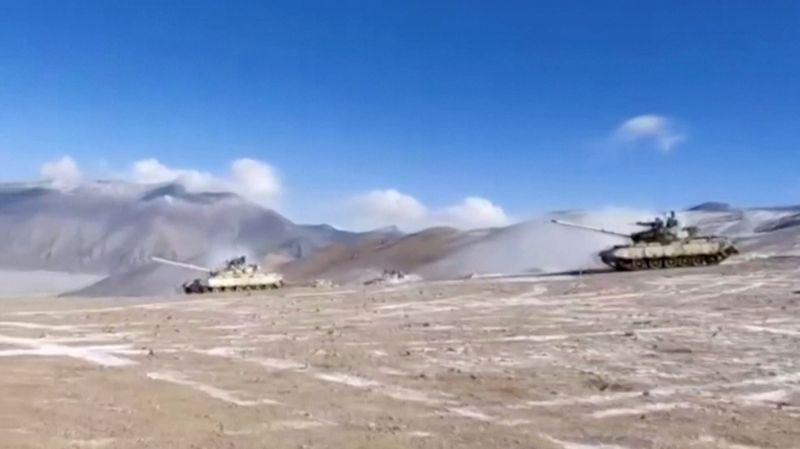
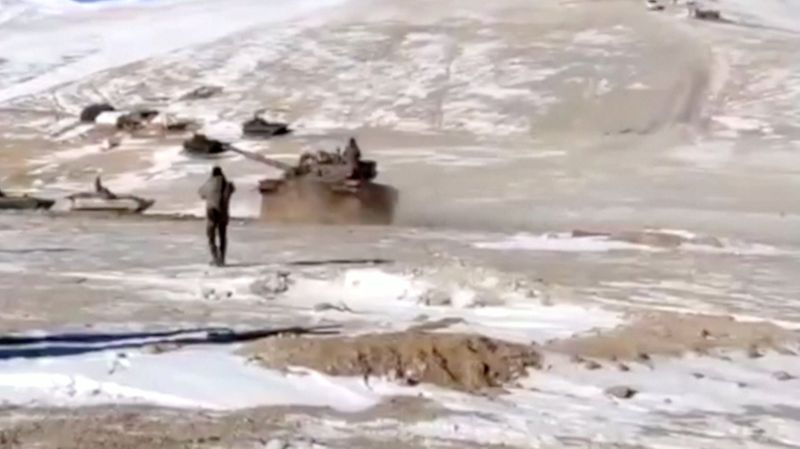
Video released by the Indian army showed troops saluting and shaking hands with each other in the barren mountains where the lake is located. A few battle tanks are seen turning around away from the frontlines.
In June, 20 Indian soldiers were killed when the two sides clashed with iron rods and stones in the Galwan Valley, the first combat losses on the border in 45 years. China also suffered an unspecified number of casualties.
Since then the two countries, who fought a war in 1962, had moved thousands of troops, tanks, artillery guns and combat jets close to the border.
Singh said the Indian government had told Beijing that peace and tranquility had been seriously disturbed by the actions of Chinese troops and bilateral ties had suffered.
“To ensure disengagement in friction points along the LAC, it was our view that troops of both sides, who are now in close proximity, should vacate the forward deployments made in 2020 and return to the permanent and accepted bases,” he said.
Pangong lake is a finger of water extending from China’s Tibet Autonomous Region in India’s Ladakh region.
In August, Indian troops occupied heights on the southern banks of the lake in retaliation against Chinese troops advancing further along the north bank.
Singh said the two sides had agreed to dismantle defence structures they had built on the two sides of the lake, two-thirds of which China controls.
Once the disengagement has been completed at the lake, military commanders will meet within 48 hours to discuss pull back from other areas, Singh said.
India and China have not been able to agree on their 3,500 km (2,200 mile) long border since the war in 1962.
(Reporting by Sanjeev Miglani; Editing by Kim Coghill, Lincoln Feast and Michael Perry)