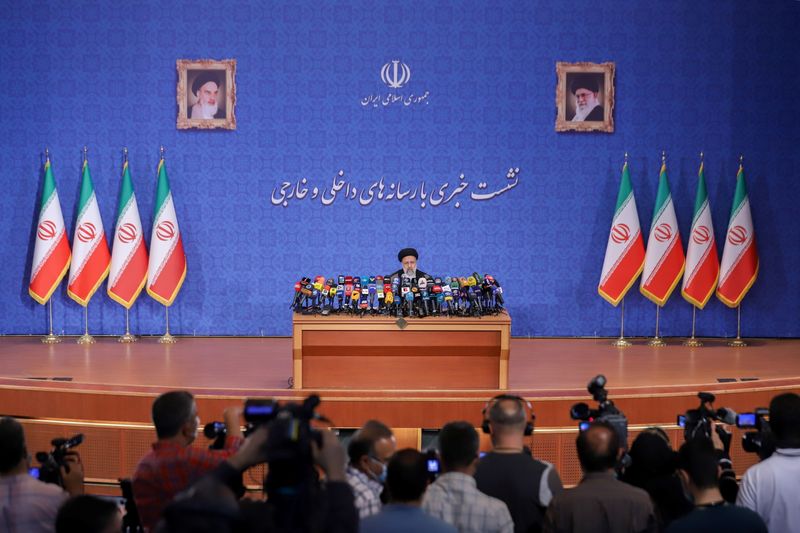
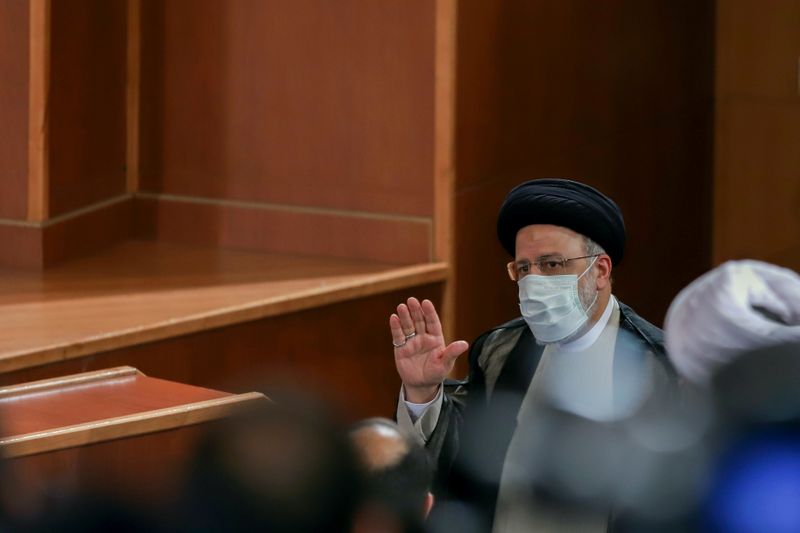
DUBAI/WASHINGTON (Reuters) – Iranian President-elect Ebrahim Raisi on Monday backed talks between Iran and six world powers to revive a 2015 nuclear deal but flatly rejected meeting U.S. President Joe Biden, even if Washington removed all sanctions.
In his first news conference since winning Friday’s presidential election, the hardline judge said his foreign policy priority would be improving ties with Iran’s Gulf Arab neighbours, while calling on Iran’s regional rival Saudi Arabia to immediately halt its intervention in Yemen.
Raisi, 60, a strident critic of the West, will take over from pragmatist Hassan Rouhani on Aug. 3 as Iran seeks to salvage the tattered nuclear deal and be rid of punishing U.S. sanctions that have crippled Iran’s economy.
“We support the negotiations that guarantee our national interests. … America should immediately return to the deal and fulfil its obligations under the deal,” said Raisi, who is himself under U.S. sanctions.
Negotiations have been under way in Vienna since April to work out how Iran and the United States can both return to compliance with the nuclear pact, which Washington abandoned in 2018 under then-President Donald Trump before reimposing sanctions on Iran.
Iran has subsequently breached the deal’s limits on enrichment of uranium, designed to minimise the risk of it developing nuclear weapons potential. Tehran has long denied having any such ambition.
Raisi said Iran’s foreign policy would not be limited to the nuclear deal, adding that “all U.S. sanctions must be lifted and verified by Tehran”.
Iranian and Western officials alike say Raisi’s rise is unlikely to alter Iran’s negotiating stance in talks to revive the nuclear deal. Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei has the final say on all major policy.
Asked if he would meet Biden if those sanctions were lifted, Raisi answered: “No.”
WHITE HOUSE RESPONSE
The White House downplayed Raisi’s influence, saying no meeting was planned and that Khamenei was the real decision maker in Tehran.
“We don’t currently have any diplomatic relations with Iran or any plans to meet at the leader level,” White House press secretary Jen Psaki told reporters. “Our view is that the decision maker here is the supreme leader.”
The U.S. State Department said it regarded the process that elected Raisi as “pretty manufactured” and expected the Vienna nuclear talks to resume “in the coming days.”
Raisi secured victory as expected in the election after a contest marked by voter apathy over economic hardships and political restrictions.
He is under U.S. sanctions over a past that includes what the United States and human rights groups say was his involvement in the extrajudicial killing of thousands of political prisoners in the Islamic Republic in 1988.
When asked about human rights groups’ allegations that he was involved in the killings, he said: “If a judge, a prosecutor has defended the security of the people, he should be praised.”
“I am proud to have defended human rights in every position I have held so far,” Raisi said.
The White House said it would keep human rights on the table following negotiations on the nuclear deal. Psaki declined to predict when or if a deal would be reached, adding that officials are “looking forward to seeing where that goes.”
Gulf Arab states have said it would be dangerous to separate the nuclear pact from Iran’s missile programme and “destabilising” behaviour in the Middle East, where Tehran and Riyadh have fought decades of proxy wars, in countries from Yemen to Iraq.
Echoing Khamenei’s stance, Raisi said Iran’s “regional activities and ballistic missile programme” were non-negotiable.
A Saudi-led coalition intervened in Yemen’s war in 2015 after Iran-backed Houthi forces drove its government out of the capital, Sanaa. The conflict has been largely stalemated for several years.
“They (the United States) did not comply with the previous agreement. How do they want to enter into new discussions?” Raisi said.
Sunni Muslim Saudi Arabia and Shi’ite Iran, which severed ties in 2016, began direct talks in Iraq in April aimed at containing tensions. “The reopening of the Saudi Embassy is not a problem for Iran,” said Raisi.
(Reporting by Parisa Hafezi in Dubai; Additional reporting by Trevor Hunnicutt in Washington; Writing by Raya Jalabi and Parisa Hafezi; Editing by Mark Heinrich, Timothy Heritage and Peter Cooney)