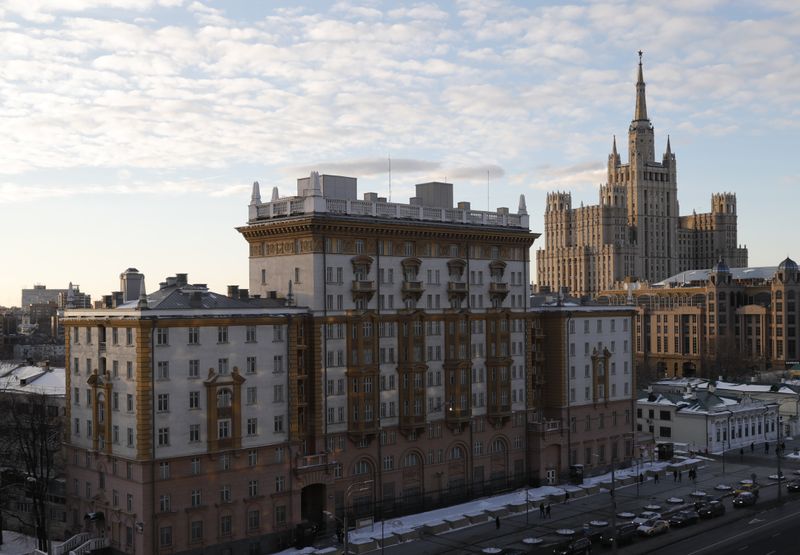
MOSCOW (Reuters) -The Kremlin accused Washington on Friday of fuelling tension with “unfriendly actions” after the U.S. embassy in Moscow said it was cutting staff and stopping processing visas for most Russians.
The embassy said it was cutting consular staff by 75% and that from May 12 it would stop processing non-immigrant visas for non-diplomatic travel after a new Russian law imposed limits on how many local staff can work at foreign diplomatic missions.
That means Russians, who are not diplomats or green card seekers, will no longer be able to apply inside their own country for visas to visit the United States for tourism and other purposes. They will have to make such applications in third countries instead if they need to.
The Russian foreign ministry pointed out that Russian consulates in the United States were still issuing visas within 10 days despite suffering diplomatic cutbacks themselves and said there was nothing to stop Washington from topping up staff by bringing in U.S. nationals.
It said the U.S. diplomatic staff quota in Russia stood at 455, but that there were only 280 accredited employees, giving Washington ample room to top up staff numbers.
Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov said the embassy’s decision would have little practical impact because, he said, Russians have already been struggling to get U.S. visas.
“You know, here one has to look at the root cause of the tense situation that is developing in our bilateral relations,” Peskov told reporters.
“If you unravel the knot of unfriendly steps in the opposite direction, then it becomes obvious that the precursor to all of this is the unfriendly actions of the United States.”
He said Russia had “expected better” of the first 100 days of Joe Biden’s U.S. presidency.
He welcomed moves to extend the New START nuclear arms treaty. “But this positive baggage is still small in comparison with the load of negativity that we have accumulated over these 100 days. This load unfortunately prevails,” he said.
Moscow and Washington have long differed over a range of issues, but ties slumped further after Biden said he believed President Vladimir Putin was “a killer”.
SANCTIONS
The United States imposed sanctions on Russia this month for alleged malign activity, including interfering in last year’s U.S. election, cyber hacking and “bullying” neighbouring Ukraine.
Moscow retaliated with sanctions against the United States, and has rejected U.S. criticism of its treatment of jailed Kremlin critic Alexei Navalny.
Russia’s ties with several countries in central and eastern Europe have also deteriorated in recent weeks, leading to a series of diplomatic expulsions.
When Putin signed the law limiting local staff employed at diplomatic missions last week, he also told the government to draw up a list of “unfriendly” states to be subject to the restrictions.
A draft list published by Russian state TV suggests the United States is one of the countries that will be on it.
“We regret that the actions of the Russian government have forced us to reduce our consular work force by 75%,” the U.S. embassy said in a statement.
“Effective May 12, U.S. Embassy Moscow will reduce consular services offered to include only emergency U.S. citizen services and a very limited number of age-out and life or death emergency immigrant visas,” it said.
“I have always been afraid of the ‘Iron Curtain’, only now it’s not being imposed by our side, but by the other side,” said Ksenia Sobchak, a former Russian presidential candidate.
(Reporting by Anton Kolodyazhnyy; Writing by Alexander Marrow, Editing by Timothy Heritage)