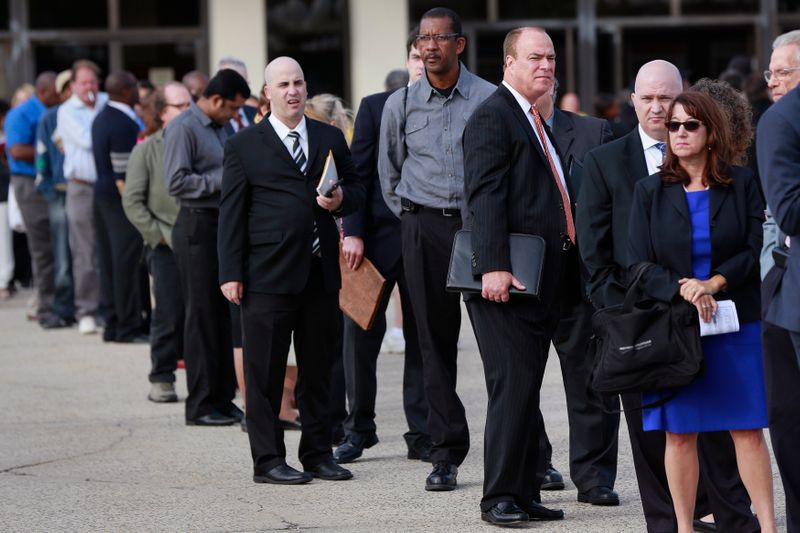
WASHINGTON (Reuters) – The number of Americans filing new claims for jobless benefits rose to a two-month high last week, stoking fears the COVID-19 pandemic was inflicting lasting damage to the labor market.
The weekly unemployment claims report from the Labor Department on Thursday, the most timely data on the economy’s health, also showed at least 25 million were on jobless benefits at the end of September. It reinforced views the economy’s recovery from the recession, which started in February, was slowing and in urgent need of another government rescue package.
The economic hardship wrought by the coronavirus crisis is a major hurdle to President Donald Trump’s chances of getting a second term in the White House when Americans go to the polls on Nov. 3. Former Vice President Joe Biden, the Democratic Party’s candidate, has blamed the Trump administration’s handling of the pandemic for the worst economic turmoil in at least 73 years.
“The increase in initial claims is disturbing,” said Chris Low, chief economist at FHN in New York. “It is difficult to see it and not think the recovery is vulnerable.”
Initial claims for state unemployment benefits increased 53,000 to a seasonally adjusted 898,000 for the week ended Oct. 10. Data for the prior week was revised to show 5,000 more applications received than previously reported.
Economists polled by Reuters had forecast 825,000 applications in the latest week. The surprise increase came even as California processed no claims. California, the most populous state in the nation, suspended the processing of new applications for two weeks in late September to combat fraud. It resumed accepting claims last Monday.
Graphic: Jobless claims https://graphics.reuters.com/USA-STOCKS/xklpymgympg/joblessclaims.png
Unadjusted claims rose 76,670 to 885,885 last week. Economists prefer the unadjusted number given earlier difficulties adjusting the claims data for seasonal fluctuations because of the economic shock caused by the pandemic. Including a government-funded program for the self-employed, gig workers and others who do not qualify for the regular state unemployment programs, 1.3 million people filed claims last week.
Seven months into the pandemic in the United States, first-time claims remain well above their 665,000 peak during the 2007-09 Great Recession, though below a record 6.867 million in March. With new COVID-19 cases surging across the country and the White House and Congress struggling to agree on another rescue package for businesses and the unemployed, claims are likely to remain elevated.
Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin said on Thursday he would keep trying to reach a deal with House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, a Democrat, before next month’s election.
Stocks on Wall Street were lower. The dollar gained versus a basket of currencies. U.S. Treasury prices rose.
MILLIONS EXHAUST BENEFITS
About 3.8 million people had permanently lost their jobs in September, with another 2.4 million unemployed for more than six months. Economists fear those numbers could swell.
Though the claims report showed a decline in the number of people on unemployment rolls in early October, economists said that was because many people had exhausted their eligibility for benefits, which are limited to six months in most states.
The number of people receiving benefits after an initial week of aid declined 1.165 million to 10.018 million in the week ending Oct. 3.
About 2.8 million workers filed for extended unemployment benefits in the week ending Sept. 26, up 818,054 from the prior week. That was the largest weekly gain since the program’s launch last spring. These benefits are set to expire on Dec. 31.
Tens of thousands of airline workers have been furloughed. State and local government budgets have been crushed by the pandemic, leading to layoffs that are expected to escalate without help from the federal government.
“Risks to the labor market outlook are weighted heavily to the downside,” said Ryan Sweet, a senior economist at Moody’s Analytics in West Chester, Pennsylvania. “The increased spread of the virus across much of the country could result in an even larger pullback in business activity than expected.”
Though economic activity rebounded in the third quarter because of fiscal stimulus, the stubbornly high jobless claims suggest momentum ebbed heading into the fourth quarter.
Other reports on Thursday showed mixed fortunes for regional manufacturing in October. A survey from the New York Federal Reserve showed its business conditions index fell seven points to a reading of 10.5 this month. Companies reported continued gains in new orders and shipments, though unfilled orders maintained their decline. Factory employment rose modestly, but the average workweek increased significantly.
Separately, the Philadelphia Fed said its business conditions index jumped to a reading of 32.3 from 15.0 in September. Measures of new orders and shipments at factories in the region that covers eastern Pennsylvania, southern New Jersey and Delaware rose. A gauge of factory employment fell, but manufacturers increased hours for workers.
Third-quarter GDP growth estimates are topping a 32% annualized rate. The economy contracted at a 31.4% pace in the second quarter, the deepest decline since the government started keeping records in 1947. Growth estimates for the fourth quarter have been cut to as low as a 2.5% rate from above a 10% pace.
(Reporting by Lucia Mutikani; Editing by Chizu Nomiyama and Andrea Ricci)