(Reuters) – Over about eight years, the American drugstore chain Rite Aid Corp <RAD.N> quietly added facial recognition systems to 200 stores across the United States, in one of the largest rollouts of such technology among retailers in the country, a Reuters investigation found.
In the hearts of New York and metro Los Angeles, Rite Aid deployed the technology in largely lower-income, non-white neighborhoods, according to a Reuters analysis. And for more than a year, the retailer used state-of-the-art facial recognition technology from a company with links to China and its authoritarian government.
In telephone and email exchanges with Reuters since February, Rite Aid confirmed the existence and breadth of its facial recognition program. The retailer defended the technology’s use, saying it had nothing to do with race and was intended to deter theft and protect staff and customers from violence. Reuters found no evidence that Rite Aid’s data was sent to China.
Last week, however, after Reuters sent its findings to the retailer, Rite Aid said it had quit using its facial recognition software. It later said all the cameras had been turned off.
“This decision was in part based on a larger industry conversation,” the company told Reuters in a statement, adding that “other large technology companies seem to be scaling back or rethinking their efforts around facial recognition given increasing uncertainty around the technology’s utility.”
Reuters pieced together how the company’s initiative evolved, how the software has been used and how a recent vendor was linked to China, drawing on thousands of pages of internal documents from Rite Aid and its suppliers, as well as direct observations during store visits by Reuters journalists and interviews with more than 40 people familiar with the systems’ deployment. Most current and former employees spoke on condition of anonymity, saying they feared jeopardizing their careers.
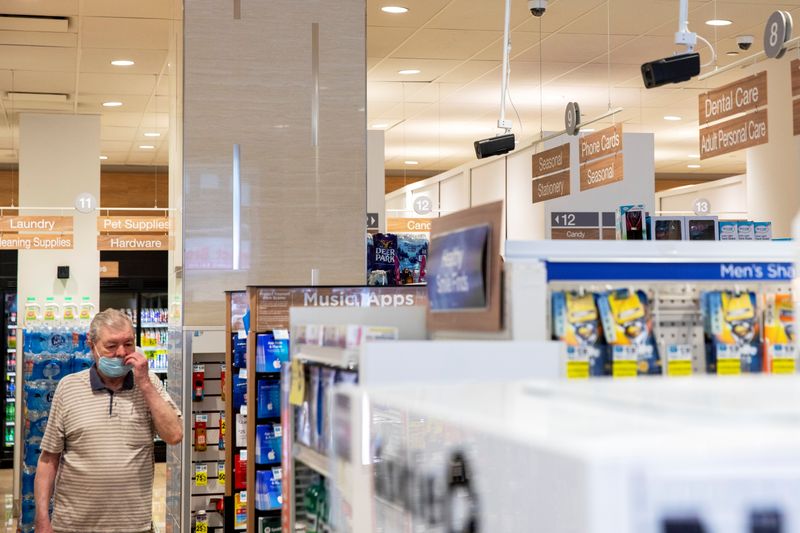
While Rite Aid declined to disclose which locations used the technology, Reuters found facial recognition cameras at 33 of the 75 Rite Aid shops in Manhattan and the central Los Angeles metropolitan area during one or more visits from October through July.
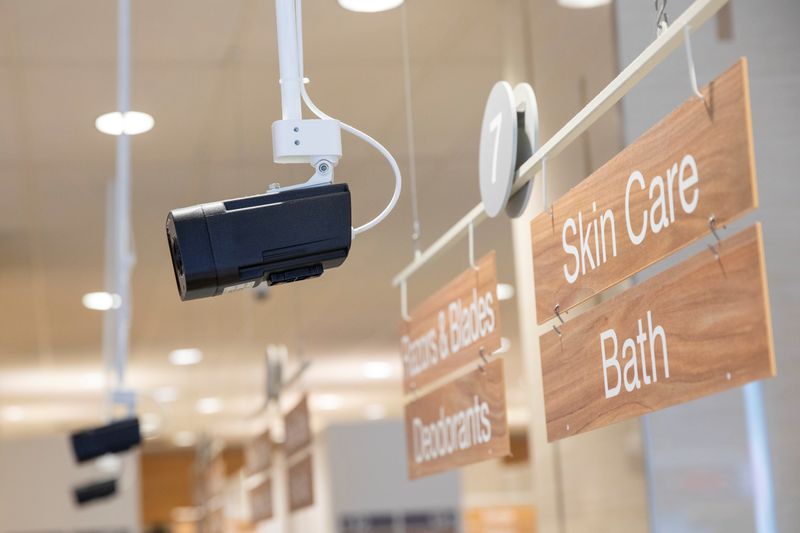
The cameras were easily recognizable, hanging from the ceiling on poles near store entrances and in cosmetics aisles. Most were about half a foot long, rectangular and labeled either by their model, “iHD23,” or by a serial number including the vendor’s initials, “DC.” In a few stores, security personnel – known as loss prevention or asset protection agents – showed Reuters how they worked.
The cameras matched facial images of customers entering a store to those of people Rite Aid previously observed engaging in potential criminal activity, causing an alert to be sent to security agents’ smartphones. Agents then reviewed the match for accuracy and could tell the customer to leave.
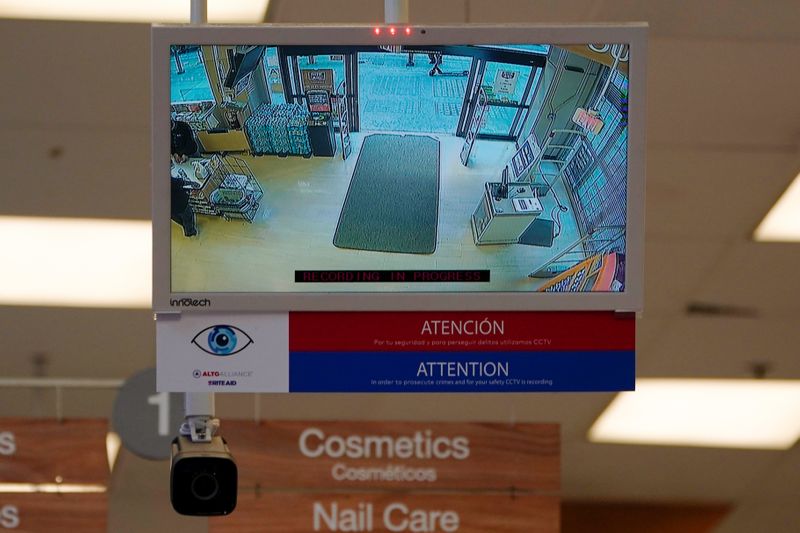
Rite Aid told Reuters in a February statement that customers had been apprised of the technology through “signage” at the shops, as well as in a written policy posted this year on its website. Reporters found no notice of the surveillance in more than a third of the stores they visited with the facial recognition cameras.
Among the 75 stores Reuters visited, those in areas that were poorer or less white were much more likely to have the equipment, the news agency’s statistical analysis found.
Stores in more impoverished areas were nearly three times as likely as those in richer areas to have facial recognition cameras. Seventeen of 25 stores in poorer areas had the systems. In wealthier areas, it was 10 of 40. (Ten of the stores were in areas whose wealth status was not clear. Six of those stores had the equipment.)
In areas where people of color, including Black or Latino residents, made up the largest racial or ethnic group, Reuters found that stores were more than three times as likely to have the technology.
Reuters’ findings illustrate “the dire need for a national conversation about privacy, consumer education, transparency, and the need to safeguard the Constitutional rights of Americans,” said Carolyn Maloney, the Democratic chairwoman of the House oversight committee, which has held hearings on the use of facial recognition technology.
Rite Aid said the rollout was “data-driven,” based on stores’ theft histories, local and national crime data and site infrastructure.
Cathy Langley, Rite Aid’s vice president of asset protection, said earlier this year that facial recognition – which she referred to as “feature matching” – resulted in less violence and organized crime in the company’s stores. Last week, however, Rite Aid said its new leadership team was reviewing practices across the company, and “this was one of a number of programs that was terminated.”
‘ORWELLIAN SURVEILLANCE’
Facial recognition technology has become highly controversial in the United States as its use has expanded in both the public and private sectors, including by law enforcement and retailers. Civil liberties advocates warn it can lead to harassment of innocent individuals, arbitrary and discriminatory arrests, infringements of privacy rights and chilled personal expression.
Adding to these concerns, recent research by a U.S. government institute showed that algorithms that underpin the technology erred more often https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-crime-face/u-s-government-study-finds-racial-bias-in-facial-recognition-tools-idUSKBN1YN2V1 when subjects had darker skin tones.
Facial recognition systems are largely unregulated in the United States, despite disclosure or consent requirements, or limits on government use, in several states, including California, Washington, Texas and Illinois. Some cities, including San Francisco, ban municipal officials from using them. In general, the technology makes photos and videos more readily searchable, allowing retailers almost instantaneous facial comparisons within and across stores.
Among the systems used by Rite Aid was one from DeepCam LLC, which worked with a firm in China whose largest outside investor is a Chinese government fund. Some security experts said any program with connections to China was troubling because it could open the door to aggressive surveillance in the United States more typical of an autocratic state.
U.S. Senator Marco Rubio, a Florida Republican and acting chair of the U.S. Senate’s intelligence committee, told Reuters in a statement that the Rite Aid system’s potential link to China was “outrageous.” “The Chinese Communist Party’s buildup of its Orwellian surveillance state is alarming, and China’s efforts to export its surveillance state to collect data in America would be an unacceptable, serious threat,” he said.
The security specialists expressed concern that information gathered by a China-linked company could ultimately land in that government’s hands, helping Beijing to refine its facial recognition technology globally and monitor people in ways that violate American standards of privacy.
“If it goes back to China, there are no rules,” said James Lewis, the Technology Policy Program director at the Washington-based Center for Strategic and International Studies.
Asked for comment, China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs said: “These are unfounded smears and rumors.”
‘A PROMISING NEW TOOL’
Rite Aid, afflicted with financial losses in recent years, is not the only retailer to adopt or explore facial recognition technology.
Two years ago, the Loss Prevention Research Council, a coalition founded by retailers to test anti-crime techniques, called facial recognition “a promising new tool” worthy of evaluation.
“There are a handful of retailers that have made the decision, ‘Look, we need to leverage tech to sell more and lose less,” said council director Read Hayes. Rite Aid’s program was one of the largest, if not the largest, in retail, Hayes said. The Camp Hill, Pennsylvania-based company operates about 2,400 stores around the country.
The Home Depot Inc <HD.N> said it had been testing facial recognition to reduce shoplifting in at least one of its stores but stopped the trial this year. A smaller rival, Menards, piloted systems in at least 10 locations as of early 2019, a person familiar with that effort said.
Walmart Inc <WMT.N> has also tried out facial recognition in a handful of stores, said two sources with knowledge of the tests. Walmart and Menards had no comment.
Using facial recognition to approach people who previously have committed “dishonest acts” in a store before they do so again is less dangerous for staff, said Rite Aid’s former vice president of asset protection, Bob Oberosler, who made the decision to deploy an early facial recognition system at Rite Aid. That way, “there was significantly less need for law enforcement involvement,” he said.
‘TOUGHER’ NEIGHBORHOODS
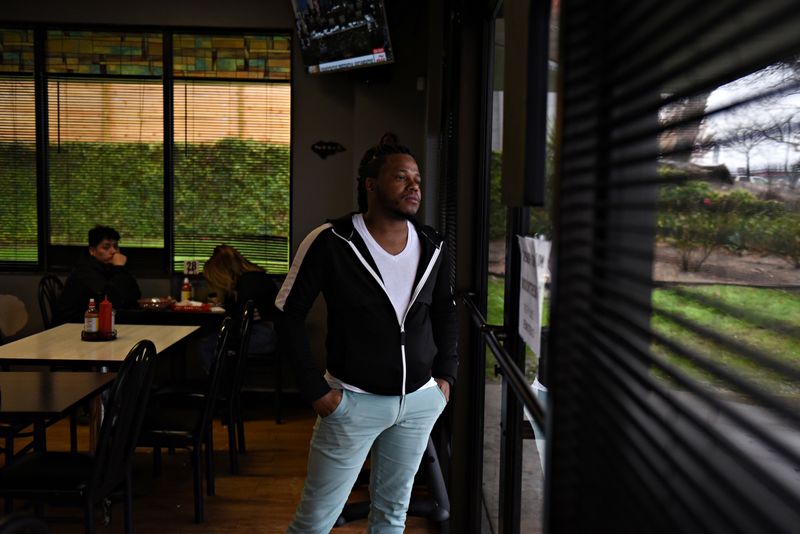
In interviews, 10 current and former Rite Aid loss prevention agents told Reuters that the system they initially used in stores was from a company called FaceFirst, which has been backed by U.S. investment firms.
It regularly misidentified people, all 10 of them said.
“It doesn’t pick up Black people well,” one loss prevention staffer said last year while using FaceFirst at a Rite Aid in an African-American neighborhood of Detroit. “If your eyes are the same way, or if you’re wearing your headband like another person is wearing a headband, you’re going to get a hit.”
FaceFirst’s chief executive, Peter Trepp, said facial recognition generally works well irrespective of skin tone, an issue he said the industry addressed years ago. He declined to talk about Rite Aid, saying he would not discuss any possible clients.
Rite Aid originally piloted FaceFirst at its store on West 3rd Street and South Vermont Avenue in Los Angeles, a largely Asian and Latino neighborhood, around 2012.
Of the 65 stores the retailer targeted in its first big rollout, 52 were in areas where the largest group was Black or Latino, according to Reuters’ analysis of a Rite Aid planning document from 2013 that was read aloud to a reporter by someone with access to it. Reuters confirmed that some of these stores later deployed the technology but did not confirm its presence at every location on the list.
Separately, two former Rite Aid managers and a third source familiar with the FaceFirst rollout said the systems were concentrated, respectively, in the “tougher,” “toughest” or “worst” areas.
Reuters reviewed a 2016 spreadsheet from the company’s asset protection unit in which Rite Aid rated 20 higher-earning Manhattan stores as having equal risk of loss – labeled “MedHigh.” Two of 10 stores where whites were the largest racial group had facial recognition technology when Reuters visited this year, whereas eight of the 10 in non-white areas had the systems.
One spot ranked “MedHigh” was a store at 741 Columbus Avenue in New York’s whiter, wealthier Upper West Side. Another was the pharmacy’s West 125th Street store in nearby Harlem, a majority African-American neighborhood. The Harlem store got facial recognition technology; the Upper West Side one did not, as of July 9.
(See graphics here https://tmsnrt.rs/2EpMRhF?losangeles=true and here https://tmsnrt.rs/2EpMRhF?manhattan=true and here https://tmsnrt.rs/2EpMRhF?scatter=true)
‘LOOKS NOTHING LIKE ME’
Starting in 2013, as Rite Aid deployed FaceFirst’s technology in Philadelphia, Baltimore and beyond, some serious drawbacks emerged, current and former security agents and managers told Reuters.
For instance, the system would “generate 500 hits in an hour all across the United States” when photos in the system were blurry or taken at an odd angle, one of the people familiar with FaceFirst’s operations said.
FaceFirst’s Trepp said the company has high accuracy rates while running “over 12 trillion comparisons per day without any known complaints to date.”
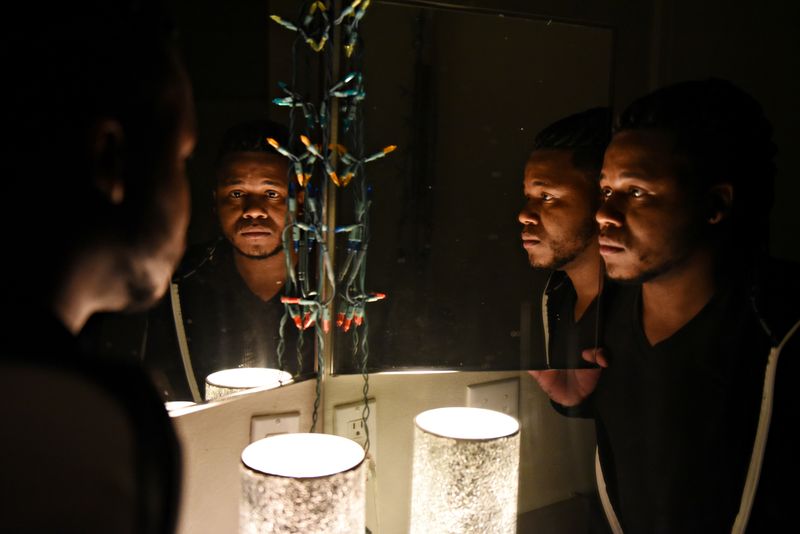
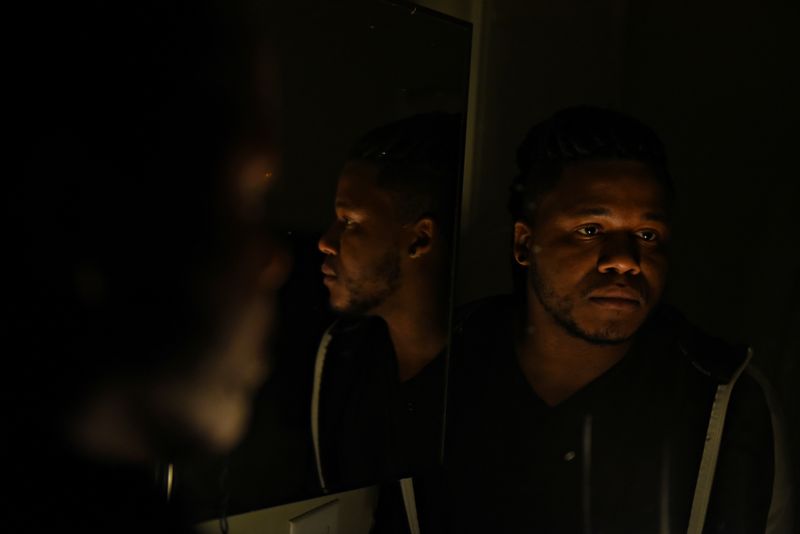
During that earlier period, Tristan Jackson-Stankunas said Rite Aid wrongly fingered him as a shoplifter in a Los Angeles store based on someone else’s photo. While Reuters could not confirm the method Rite Aid used to identify him, the store had FaceFirst technology by that time, according to a Rite Aid security agent and a Foursquare review photo showing the camera.
According to a complaint Jackson-Stankunas filed with the California Department of Consumer Affairs a week after the incident, he was looking for air freshener in September 2016 when a manager ordered him to leave the store. The manager said he had received a security image of Jackson-Stankunas taken at another Rite Aid in 2013 from which he allegedly had stolen goods, according to the complaint.
When Jackson-Stankunas viewed the photo on the manager’s phone, he told Reuters, he saw nothing in common with the person except their race: Both are Black.
“The guy looks nothing like me,” said Jackson-Stankunas, 34, who ultimately was allowed to make his purchase and leave the store. Rite Aid “only identified me because I was a person of color. That’s it.”
The California department told him his complaint fell outside its purview, directing him to another state office, email records show. Instead, he said he decided to write the store a bad review on Yelp.
Rite Aid and the manager who allegedly was involved declined to comment on Jackson-Stankunas’ account.
At one store Reuters visited, a security agent scrolled through FaceFirst “alerts” showing a number of cases in which faces were obviously mismatched, including a Black man mixed up with someone who was Asian. Reuters could not determine whether the incorrect matches resulted in confrontations with customers.
FaceFirst CEO Trepp said that his company takes racial bias seriously and would not work with any business that disregarded civil rights. “We cannot stand for racial injustice of any kind, including in our technology,” he said.
Generally, Trepp said, Reuters’ findings about his company contained “extensive factual inaccuracies” and are “not based upon information from credible sources.”
A NEW SYSTEM
Early in 2018, Rite Aid began installing technology from DeepCam LLC, ultimately phasing out FaceFirst in stores around the country, interviews with Rite Aid loss prevention agents and internal vendor documents indicate.
Six security staffers who used both systems said DeepCam’s matches were more accurate – sometimes to a fault. The technology picked up faces from ads on buses or pictures on T-shirts, three said. One famous face captured in DeepCam was Marilyn Monroe’s, one of the agents said.
At least until 2017, FaceFirst had employed an older method of biometric identification that compared maps of subjects’ faces, two people familiar with its system said. Only later did it move over to software based on “artificial intelligence” like DeepCam’s. Though the data and algorithms differ by brand, these systems draw upon potentially millions of samples to “learn” how to match faces.
DeepCam cameras photographed and took live video of every person entering a Rite Aid store, aiming to create a unique facial profile, Rite Aid agents said. If the customer walked in front of another DeepCam facial recognition camera at a Rite Aid shop, new images were added to the person’s existing profile. Two agents said they lost access to the images after 10 days unless the person landed on a watch list based on their behavior in stores.
When agents saw someone commit a crime – or just do something suspicious, one said – they scrolled through profiles on their smartphone to search for the individual, only adding the person to the watch list with a manager’s approval. The next time the shopper walked into a Rite Aid that had the technology, agents received a phone alert and checked the match for accuracy. Then they could order the person to leave, agents told Reuters.
Rite Aid said adding customers to the watch list was based on “multiple layers of meaningful human review.” The company told Reuters its procedures ensured customers were not confronted unnecessarily.
If a person was found to be engaging in criminal behavior, Rite Aid said, “we retain the data as a matter of policy to cooperate in pending or potential criminal investigations.”
Other U.S. retail stores have tried DeepCam. Independent 7-Eleven franchise owners in Virginia told Reuters they conducted trials of the software starting in 2018 and later dropped it. They said they largely found the system accurate but not user friendly and too expensive to maintain. The system was advertised online as costing $99 a month.
7-Eleven Inc did not answer requests for comment.
THE CHINA CONNECTION
The two founding owners of U.S.-based DeepCam LLC were Don Knasel and Jingfeng Liu, who set up the firm in Longmont, Colorado, in 2017, state records show. Liu’s residential address in Longmont was listed as its headquarters.
A Chinese native with U.S. citizenship and a doctorate from Carnegie Mellon University, Liu had the skills to do business in both the United States and China.
According to China’s official business registration records, he is chairman of another facial recognition firm in China called Shenzhen Shenmu Information Technology Co Ltd, whose website is DeepCam.com.
For a time, the U.S.-based DeepCam LLC and Shenzhen Shenmu were closely connected: In addition to Liu’s role in both companies, they shared the same website and email accounts, according to internal records seen by Reuters.
Internal correspondence reviewed by Reuters suggests that DeepCam reached a deal with Rite Aid by March 2018, when a colleague emailed Knasel to congratulate him. Internal records also indicated that China-based Shenzhen Shenmu helped its American counterpart with product development and that Liu was expected to pay at least some of the bills. That same month, a U.S. executive wrote: “Hi Jingfeng- Thanks for the credit card. Here is the receipt for the Indianapolis Trade Show.”
In an interview, Liu confirmed the financing, saying of Knasel: “Whenever he needed money, I give him some money.” Liu said Knasel told him about the Rite Aid project but left him in the dark about the business. Knasel “never let data cross between the two countries,” Liu said.
As the Rite Aid rollout proceeded in 2018, correspondence among DeepCam staff, seen by Reuters, expressed concerns about publicly revealing any links to China, as well as using the term “facial recognition” in the U.S. market for fear of attracting the attention of the American Civil Liberties Union.
Days after the ACLU wrote a March 2018 blog post https://www.aclu.org/blog/privacy-technology/surveillance-technologies/are-stores-you-shop-secretly-using-face critical of retailers’ suspected use of the technology, including Rite Aid’s, Knasel emailed staff: “It looks like the ACLU may be starting to stick its head up….We need to tone down facial recognition, which I have tried to do….If they come after us, we are dead….so we have to avoid.” The punctuation in the message is Knasel’s.
Jay Stanley, the ACLU senior policy analyst who co-authored the blog post, told Reuters that the right response to civil liberties concerns about surveillance technology “is not to start using it in secret.”
It is “to stop using the technology altogether. We are glad Rite Aid seems to have ultimately recognized this.”
Today, both Liu and Knasel say no ties exist between the U.S. and Chinese businesses.
“We never do any business in USA,” Liu wrote in a brief email to Reuters in March. “We focus in China market.”
More recently, in an interview and an email, Liu said he had not spoken with Knasel for more than a year and, to his disappointment, had not benefited from the U.S. venture.
In a statement to Reuters, Knasel sought to distance himself from Liu, Shenzhen Shenmu and DeepCam.
He did not address questions about DeepCam’s deal with Rite Aid. DeepCam, he said, is “winding up” its operations and now has no assets. He added that DeepCam never supplied China-based Shenzhen Shenmu with any data.
In February, Rite Aid told Reuters that DeepCam had been “re-branded” as pdActive. PdActive is a facial recognition company run by Knasel, who said it is not a rebranding of DeepCam but a different company that has no owners who are Chinese citizens.
Knasel remained connected to DeepCam through another company he runs, dcAnalytics, which Knasel said licensed DeepCam’s technology until November 2019. Since then, Knasel said, U.S.-based dcAnalytics has been using “proprietary” technology, as well as facial recognition cameras purchased from DeepCam.
Knasel said dcAnalytics is “committed to upholding the highest standards possible to make sure facial recognition technology is used fairly, properly and responsibly.”
SENSITIVE QUESTIONS
Steve Dickinson, a Seattle attorney who practiced law in China for more than a decade and writes about cybersecurity, said geopolitical tensions have added sensitivity to any work Chinese surveillance firms do in the United States.
Last year, the U.S. government blacklisted several Chinese companies – including Hikvision <002415.SZ>, one of the biggest surveillance camera manufacturers globally – alleging involvement in human rights abuses. China has deployed facial recognition cameras widely within its borders, providing a level of monitoring unfathomable to many Americans.
At the time, a U.S. Hikvision spokesman said the firm “strongly opposes” the decision and that punishing Hikvision would harm its U.S. business partners and discourage global companies from communicating with the U.S. government.
Liu described his company as nothing like the Chinese video surveillance giants. With about 20 employees, he said, it is “a tiny company pretending to be big,” struggling unsuccessfully to get government contracts and nearly bankrupt.
Reuters found that he and his company have financial and other ties to the Chinese government, however.
Most notably, Shenzhen Shenmu’s largest outside investor, holding about 20% of its registered capital, is a strategic fund set up by the government of China. Called the SME Development Fund (Shenzhen Limited Partnership), it has built a 6 million yuan ($855,000) stake in Shenzhen Shenmu since early 2018, Chinese public business records show.
A person with the same name as a Shenzhen Shenmu board director has also worked for the venture firm managing the SME fund, according to the records and the investment firm’s website.
The fund acknowledged investing in Shenzhen Shenmu and said it “does not participate in the daily operation and management of the enterprise.”
Liu is a member of China’s Thousand Talents program, according to a local government website. That program was started by Beijing as a way to bring top academics working in important fields abroad back to China. According to allegations https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/harvard-university-professor-and-two-chinese-nationals-charged-three-separate-china-related by the U.S. Justice Department, the program aimed to steal foreign technology.
In a statement, China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs described such allegations as false and as “stigmatization” by the United States.
Liu told Reuters he tried to get into the program but does not know if he is. The achievement was reported in an article on Shenzhen Shenmu’s website, but Liu said he only wanted to use the distinction to help him sell products. Reuters was unable to confirm with China’s government whether Liu was a member.
Another website, that of a Shenzhen Shenmu subsidiary, Magicision, claims its technology has helped officials arrest fugitives and suspected criminals in China.
Liu was vague about the firm’s public security work, saying his company has tried unsuccessfully to get contracts with Chinese law enforcement. He called the website’s information “bullshit marketing.”
About the Chinese government’s interest in his company’s data, however, he was clear.
“The China government never care about us,” he said. “We are too small.”
“I know (the) China threat is a hot, eyeball-attractive topic. But what you have in mind is totally untrue.”
(Reporting by Jeffrey Dastin in Los Angeles and New York; Data analysis by Ryan McNeill in London; Additional reporting by Cate Cadell and Yingzhi Yang in Beijing; Engen Tham and Brenda Goh in Shanghai; Farah Master in Hong Kong; the Beijing and Shanghai newsrooms; Lucas Jackson, Aleksandra Michalska and Samuel Hart in New York; Paresh Dave in Oakland; and Tom Bergin in London; Editing by Julie Marquis and Simon Robinson)