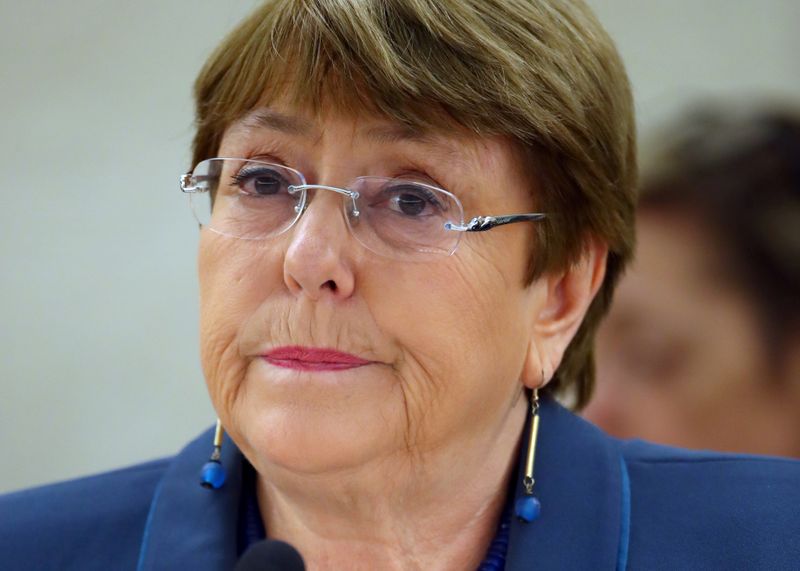
GENEVA (Reuters) – The United Nations human rights chief on Thursday urged countries to step up trials in their national courts against suspected war criminals in Syria as the conflict marks its 10th anniversary.
Attempts to refer atrocities in Syria to the International Criminal Court (ICC) in the Hague for prosecution have failed, Michelle Bachelet said.
Only one person has been convicted in a foreign court for crimes against humanity or war crimes in a conflict that has cost hundreds of thousands of lives, many of them civilians.
“It remains vital that national courts continue to conduct fair, public and transparent trials and reduce the accountability gap for such serious crimes,” Bachelet said in a statement.
Pro-democracy protests against President Bashar al-Assad’s authoritarian family rule erupted in March 2011 in southern Syria and were met by a crackdown. But they spread quickly across the country and developed into a multi-sided war that in addition to the numerous casualties has forced more than 11 million from their homes, around half the pre-war population.
Assad’s forces, backed by Iran and Russia, have recaptured many areas once held by rebel factions and Islamist militants, but the war grinds on in some corners of Syria.
It is thought that many suspected war criminals have relocated overseas.
A German court sentenced a former member of President Bashar al-Assad’s security services to 4-1/2 years in prison last month for abetting the torture of civilians, the first such verdict for crimes against humanity in the Syrian war.
Bachelet called the conviction “an important step forward on the path to justice”.
Paulo Pinheiro, chair of a team of U.N. war crimes investigators, denounced prevailing impunity.
“We commend the great courage and ingenuity of Syrian victims and activists, and the determination of some member states to bring cases where they can,” he told the Human Rights Council on Thursday.
Assad’s government has denied many previous U.N. accusations of war crimes and says it does not torture prisoners.
U.N. panel member Hanny Megally said it had been approached by 60 jurisdictions seeking information and it had provided information in about 300 ongoing cases.
(Reporting by Stephanie Nebehay; Editing by Angus MacSwan, William Maclean)