NEW YORK (Reuters) – A double whammy of economic data showing the U.S. economy in a deep downturn and reports of persistent crude oil oversupply and collapsing demand slammed global markets on Wednesday as vivid reminders of the damage from coronavirus-related lockdowns.
Oil prices sank after the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecast a 29 million-barrel-per day dive in April crude demand to levels not seen in 25 years and said no output cut could fully offset the near-term decline facing the market.
Washington could slap tariffs on U.S. oil imports if global crude producers fail to keep pledges made over the weekend to reduce output, the top U.S. energy diplomat said.
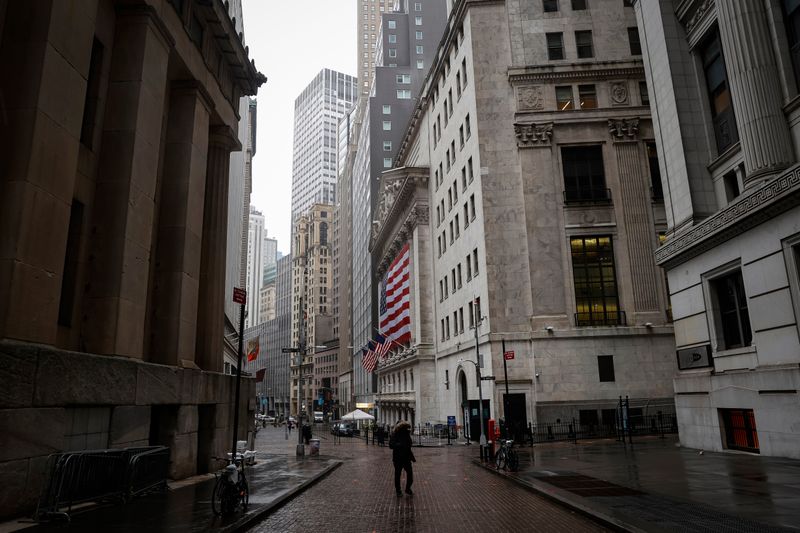
Shares on Wall Street followed European stocks lower as a raft of dour earnings from U.S. banks and a slide in listed oil heavyweights in London and Paris due to the outlook for crude prices pushed major stock indexes lower.
Uncertainty still prevails in markets as it’s not clear when economies are going to come out of the pandemic-driven slowdown, said Candice Bangsund, a global asset allocation strategist at Fiera Capital in Montreal.
“Our premise has been that uncertainty and near-term market gyrations are going to continue until we get more clarity on the status of the outbreak,” Bangsund said. “Until the virus peaks globally, there’s little visibility in that regard.”
U.S. retail sales plunged 8.7% last month, the biggest decline since the government started tracking the series in 1992, while manufacturing output dropped by the most in just over 74 years in March.
The retail sales data set U.S. consumer spending up for its worst decline in four decades.
MSCI’s gauge of stocks across the globe shed 2.16% and emerging market stocks lost 0.99%.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 445.41 points, or 1.86%, to 23,504.35. The S&P 500 lost 62.7 points, or 2.20%, to 2,783.36 and the Nasdaq Composite dropped 122.56 points, or 1.44%, to 8,393.18.
Bank of America closed down 6.5% and Citigroup Inc fell 5.6%, leading the banking subsector to slip 5.9%.
Bank earnings have been negatively impacted by a large increase in their loan loss reserves and may remain high, while operating costs may rise to deal with bad loans, said senior research analyst Dick Bove at Odeon Capital Group LLC.
The pattern could continue into 2021, he said.
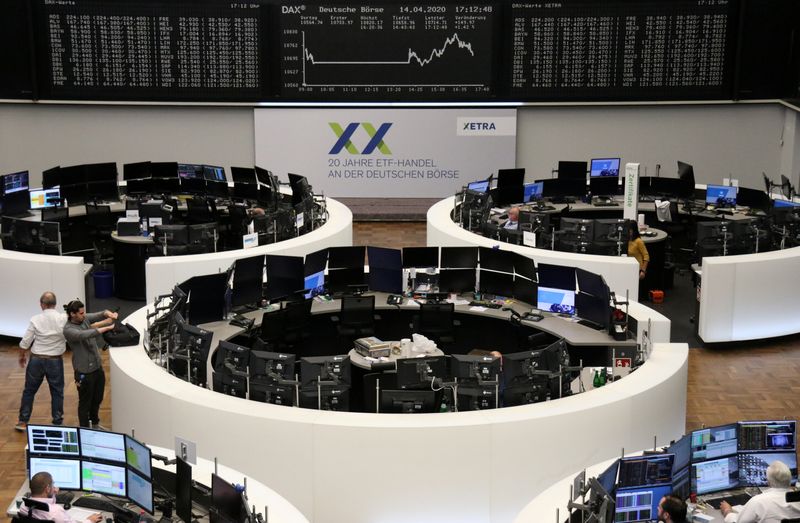
The pan-European STOXX 600 index slipped 3.3%,after rising almost 8% since April 6 on early signs thehealth crisis was ebbing and hopes sweeping lockdownmeasures would soon be lifted.
Chancellor Angela Merkel said some shops in Germany could reopen next week, but that social distancing rules would remain in place. England’s chief medical officer said that while Britain was probably close to the epidemic’s peak, it was too soon to begin thinking about next steps.
The number of COVID-19 cases reported worldwide passed 2 million on Tuesday, and the pandemic has killed 131,101, according to a Reuters tally.
Oil companies Total SA, Royal Dutch Shell Plc and BP Plc all sank in Europe, pushing the European energy index down 6.3%.
U.S. crude futures fell 1.2% to settle at $19.87 a barrel, while Brent futures fell 6.5% to settle at $27.69 a barrel.
U.S. Treasury yields fell across the board as risk aversion flared and knocked U.S. two-year yields below 0.2% for the first time in three years.
Benchmark 10-year notes rose 37/32 in price to push their yield down to 0.6348%.
The dollar firmed as investors fled risk assets for safe havens. The U.S. dollar index, which had fallen in the four previous trading days, climbed as high as 99.983.
The dollar index rose 0.708%, with the euro down 0.59% to $1.0914. The Japanese yen weakened 0.29% versus the greenback to 107.54 per dollar.
China earlier moved again to cushion its economy, cutting a key medium-term interest rate to record lows and paving the way for a similar reduction in benchmark loan rates, while reducing the amount banks must hold as reserves.
Gold prices fell, a day after scaling over seven-year highs, as the dollar firmed and investors booked profits. Concerns of a global recession put a floor under prices.
U.S. gold futures settled down 1.6% at $1,740.20 an ounce.
Graphic: World FX rates in 2020 http://fingfx.thomsonreuters.com/gfx/rngs/GLOBAL-CURRENCIES-PERFORMANCE/0100301V041/index.html
(Reporting by Herbert Lash, additional reporting by Katanga Johnson in Washington; Editing by Bernadette Baum and Jonathan Oatis)