BRUSSELS (Reuters) – The European Union aims to draw up a master military strategy document to define future threats, goals and ambitions in defence while focusing on six new areas of joint weapons development including tanks, officials and diplomats said.
The EU’s “Strategic Compass”, the closest thing the EU could have to a military doctrine and akin to NATO’s “Strategic Concept” that sets out alliance goals, is the latest step in accelerating efforts to deepen EU defence cooperation.
After four years of hostility towards NATO by U.S. President Donald Trump, the EU, led by France, wants to become a stand-alone military power in the long term, strong enough to fight on its own and potentially a more useful ally to the United States.
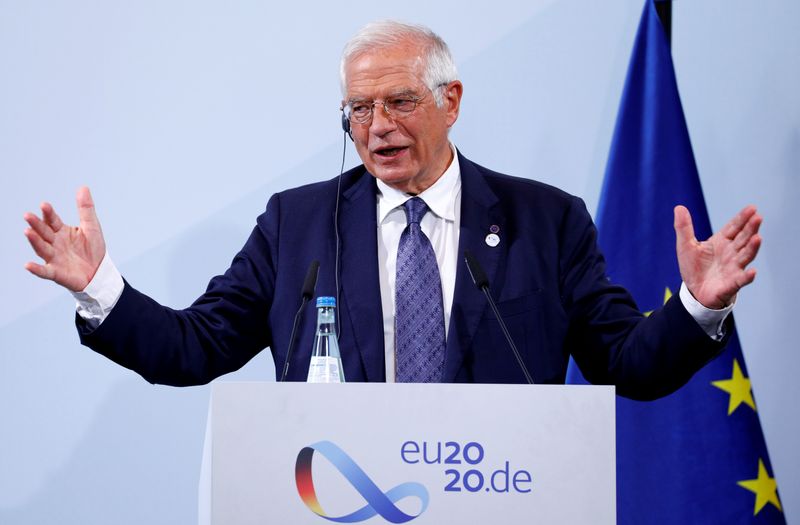
The EU’s top diplomat, Josep Borrell, will brief EU foreign ministers by video conference on Thursday on a confidential, intelligence-based threat analysis before EU defence ministers take up the work at a virtual meeting on Friday, aiming to deliver a final document in 2022.
“We need to build a compass. This is a common way of looking at the world, of defining threats and addressing them together,” said a senior EU official.
The document would not be a list of threats, in part because EU governments have different views on their gravity. Russia is seen with more alarm in the Baltics than in France, where Islamic militancy is more pressing, envoys said.
However, it does signal what Borrell has cited as “an increased momentum to strengthen our collective capacity” since a December 2017 EU defence pact to develop more firepower independently of the United States.
OPPORTUNITY FOR PARIS
Britain’s vote in 2016 to leave the EU, while depriving the bloc of a military power, has given Paris an opportunity to push longstanding ambitions for a bigger EU role in defence, with support from Berlin.
During Britain’s membership, London resisted a major military role for the EU, fearing the creation of an EU army, which officials in Brussels say is not under discussion.
Defence ministers will also receive the bloc’s first annual review on joint capabilities on Friday, which is expected to set out 100 areas for governments to develop together from 2025 over six areas, including battle tanks, maritime patrol vessels, countering drones and jamming technology.
France, Germany, Italy and Spain hope that by developing national defences together, the EU will save money by putting an end to competing national industries that duplicate weapons.
“This is not just another report”, a second senior EU official said of the first review. “This is the path for the EU to plan, spend and cooperate together in countering next-generation threats.”
(Reporting by Robin Emmott, Editing by Timothy Heritage)