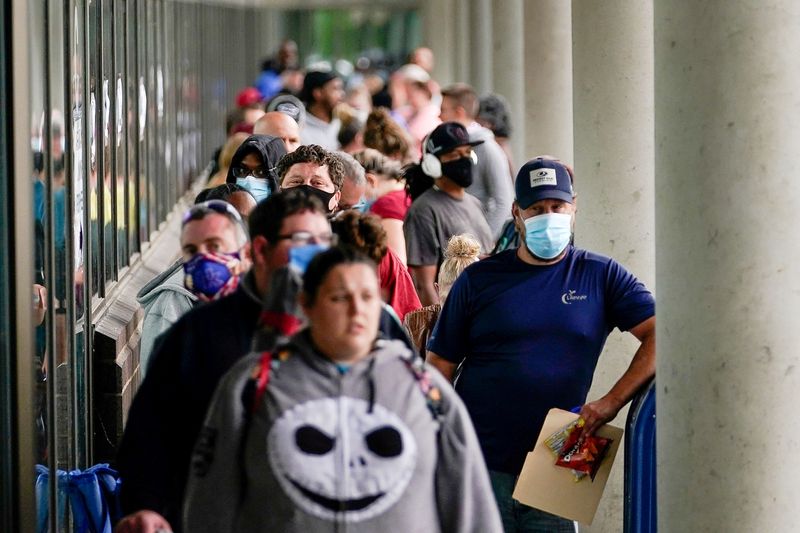
(Reuters) – Millions of Americans will see their unemployment benefits disappear at the end of the year unless Congress extends pandemic-related programs that made the aid available to a wider swath of the workforce and for a longer period of time.
The looming expiration would spark the most substantial reduction to unemployment benefits since the end of July, when a $600 weekly supplement – also added as part of the CARES Act – expired. And with coronavirus infections surging, some economists caution that job losses could rise during the winter, increasing the need for support.
Data released by the Labor Department last week showed the majority of people receiving unemployment benefits are now participating through pandemic-related programs created as part of the legislation passed by Congress in March.
Meanwhile, the number of people receiving regular unemployment benefits is declining as people facing long stretches of joblessness exhaust their state benefits and move on to pandemic programs.
(Graphic: Emergency benefits running out – https://graphics.reuters.com/USA-ECONOMY/GREATREBOOT/xklvybnolpg/USA-ECONOMY-GREATREBOOT.jpg)
If nothing changes, more than 13 million people are at risk of seeing their benefits end, potentially leaving them with less money to pay the rent, buy groceries or cover other bills. That decline in household income, combined with rising infections, could further slow consumer spending. U.S. retail sales increased 0.3% in October, less than what was expected by economists polled by Reuters.
“The bottom line is that many workers will see a massive drop in living standards and increases in poverty,” said Heidi Shierholz, director of policy for the Economic Policy Institute.
Lawmakers have to decide whether to extend two key programs. One known as pandemic unemployment assistance made unemployment benefits available to freelancers and self-employed people who wouldn’t normally be eligible.
Another program – pandemic emergency unemployment compensation – provided an additional 13 weeks of benefits for people after their state benefits ran out. More people are transferring to the pandemic emergency program as regular benefits expire.
(Graphic: Emergency benefits rising – https://graphics.reuters.com/USA-ECONOMY/PANDEMIC-BENEFITS/xklpybnllvg/chart.png_
Some may be able to receive another 13 to 20 weeks of benefits under a separate program that is not set to expire, but it is not available in all states.
Asked how he would help those facing long-term unemployment, President-elect Joe Biden on Monday called on Congress to pass the Heroes Act, a bill passed by the Democratic-controlled House of Representatives that would extend the two unemployment benefit programs, along with other assistance.
‘WE NEEDED SOMETHING STRONGER’
Some economists say the CARES Act programs patched up longstanding holes in America’s safety net for the unemployed by making jobless benefits more generous and offering them to people who wouldn’t normally qualify, including parents who cannot work during the pandemic because they have to care for children.
The benefits helped people to boost spending and pad savings and lifted millions out of poverty, even as unemployment surged, researchers found.
“There was a recognition that we needed something stronger and broader than regular (unemployment benefits), and it actually worked,” said Andrew Stettner, a senior fellow at The Century Foundation who is an expert on unemployment benefits. “Now we’re about to end it way prematurely.”
VULNERABLE POSITION
Regular unemployment benefits are typically available for up to 26 weeks in most states. Once those benefits are exhausted, job seekers can move onto the pandemic emergency unemployment assistance, to receive a total of 39 weeks of benefits.
For people who have been out of work since mid-March, those emergency benefits could expire in mid-December. People who were out of work before the current crisis started, or who live in states such as Florida or North Carolina that offer fewer weeks of state benefits, may already be approaching the end of their pandemic benefits.
Some job seekers may be able to receive what’s known as extended benefits, a pre-pandemic program that provides up to 20 weeks of additional benefits, depending on the unemployment rate in that state. But those benefits are currently not available in 13 states, according to an analysis https://www.cbpp.org/research/economy/policy-basics-how-many-weeks-of-unemployment-compensation-are-available#:~:text=Workers%20in%20most%20states%20are,Rico%2C%20and%20the%20Virgin%20Islands by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Some economists and analysts say people who lost their jobs because of the pandemic need more help as it drags on, especially those working in the hard-hit entertainment or travel industries where hiring is slow. The number of long-term unemployed – people who have been out of work for at least 27 weeks – rose to 3.6 million in October from 2.4 million in September.
The benefits cliff could “leave the economy as a whole, but particularly those who have lost their jobs and haven’t been able to land something new yet in a very vulnerable position,” said Lauren Bauer, a fellow in economic studies at the Brookings Institution.
(Graphic: More Americans face long-term unemployment – https://graphics.reuters.com/USA-ECONOMY/ygdvzklywpw/chart.png)
(Reporting by Jonnelle Marte; Editing by Paul Simao)