An iceberg about the size of Delaware is expected to break off Antarctica, the United States is no longer part of the Paris climate agreement and President Trump is all, climate change-shimate change. But no worries, as former NASA astronaut Buzz Aldrin says, we’re getting our asses to Mars, right?
Nope.
Turns out, Mars is pretty poisonous. Experiments with Martian soil have found the surface of the red planet contains a “toxic cocktail,” according to a recently published study in the journal “Scientific Reports.” The ultraviolet light that washed over the Martian landscape converts compounds in the soil into a powerful mix of bactericides.
The “toxic cocktail,” much like the cocktails that wiped our memories of Saturday night, could wipe out living organisms, effectively sterilizing the land.
“New York” magazine published a reassuring piece called “The Uninhabitable Earth” subtitled “Famine, economic collapse, a sun that cooks us: What climate change could wreak — sooner than you think.”
Here are some highlights.
Climate change means a smaller food supply.
Even when we train our eyes on climate change, we are unable to comprehend its scope. This past winter, a string of days 60 and 70 degrees warmer than normal baked the North Pole, melting the permafrost that encased Norway’s Svalbard seed vault — a global food bank nicknamed “Doomsday,” designed to ensure that our agriculture survives any catastrophe, and which appeared to have been flooded by climate change less than ten years after being built.
The article also states:
Climates differ and plants vary, but the basic rule for staple cereal crops grown at optimal temperature is that for every degree of warming, yields decline by 10 percent. Some estimates run as high as 15 or even 17 percent. Which means that if the planet is five degrees warmer at the end of the century, we may have as many as 50 percent more people to feed and 50 percent less grain to give them. And proteins are worse: It takes 16 calories of grain to produce just a single calorie of hamburger meat, butchered from a cow that spent its life polluting the climate with methane farts.
And in case you’re thinking this scenario couldn’t possibly occur:
Remember, we do not live in a world without hunger as it is. Far from it: Most estimates put the number of undernourished at 800 million globally. In case you haven’t heard, this spring has already brought an unprecedented quadruple famine to Africa and the Middle East; the U.N. has warned that separate starvation events in Somalia, South Sudan, Nigeria, and Yemen could kill 20 million this year alone.
Climate change affects human health.
In the sugarcane region of El Salvador, as much as one-fifth of the population has chronic kidney disease, including over a quarter of the men, the presumed result of dehydration from working the fields they were able to comfortably harvest as recently as two decades ago.
And this, on diseases:
There are now, trapped in Arctic ice, diseases that have not circulated in the air for millions of years — in some cases, since before humans were around to encounter them. Which means our immune systems would have no idea how to fight back when those prehistoric plagues emerge from the ice.
The Arctic also stores terrifying bugs from more recent times. In Alaska, already, researchers have discovered remnants of the 1918 flu that infected as many as 500 million and killed as many as 100 million — about 5 percent of the world’s population and almost six times as many as had died in the world war for which the pandemic served as a kind of gruesome capstone. As the BBC reported in May, scientists suspect smallpox and the bubonic plague are trapped in Siberian ice, too — an abridged history of devastating human sickness, left out like egg salad in the Arctic sun.
Also filed under “bad for all living creatures,” climate change means a loss of breathable air.
By 2090, as many as 2 billion people globally will be breathing air above the WHO “safe” level; one paper last month showed that, among other effects, a pregnant mother’s exposure to ozone raises the child’s risk of autism (as much as tenfold, combined with other environmental factors).
Could global warming cause more wars?
Climatologists are very careful when talking about Syria. They want you to know that while climate change did produce a drought that contributed to civil war, it is not exactly fair to say that the conflict is the result of warming; next door, for instance, Lebanon suffered the same crop failures. But researchers like Marshall Burke and Solomon Hsiang have managed to quantify some of the non-obvious relationships between temperature and violence: For every half-degree of warming, they say, societies will see between a 10 and 20 percent increase in the likelihood of armed conflict. In climate science, nothing is simple, but the arithmetic is harrowing: A planet five degrees warmer would have at least half again as many wars as we do today. Overall, social conflict could more than double this century. … The drowning of all American Navy bases by sea-level rise is trouble enough, but being the world’s policeman is quite a bit harder when the crime rate doubles.
And in case we weren’t completely freaking out about impending doom, there’s this…
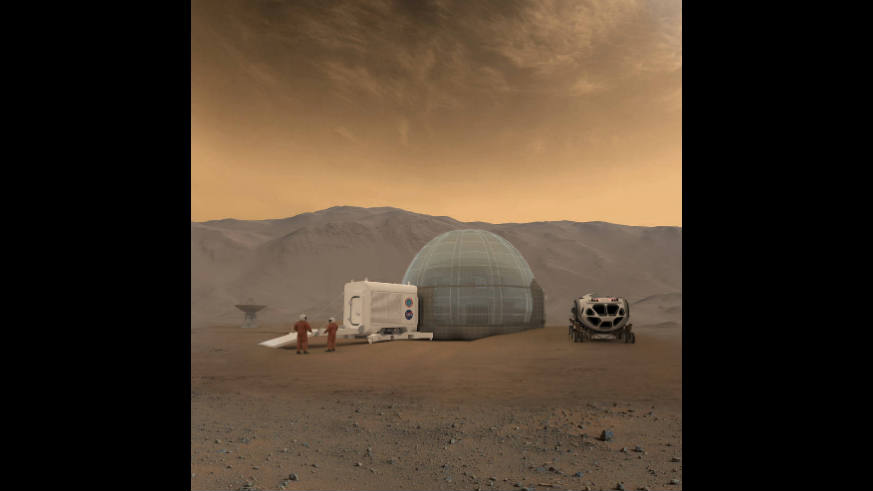
The Earth has experienced five mass extinctions before the one we are living through now, each so complete a slate-wiping of the evolutionary record it functioned as a resetting of the planetary clock, and many climate scientists will tell you they are the best analog for the ecological future we are diving headlong into. Unless you are a teenager, you probably read in your high-school textbooks that these extinctions were the result of asteroids. In fact, all but the one that killed the dinosaurs were caused by climate change produced by greenhouse gas. The most notorious was 252 million years ago; it began when carbon warmed the planet by five degrees, accelerated when that warming triggered the release of methane in the Arctic, and ended with 97 percent of all life on Earth dead. We are currently adding carbon to the atmosphere at a considerably faster rate; by most estimates, at least ten times faster. The rate is accelerating. This is what Stephen Hawking had in mind when he said, this spring, that the species needs to colonize other planets in the next century to survive, and what drove Elon Musk, last month, to unveil his plans to build a Mars habitat in 40 to 100 years.
But the dusty surface of Mars is basically poison to life, according to the recent study.
Great.