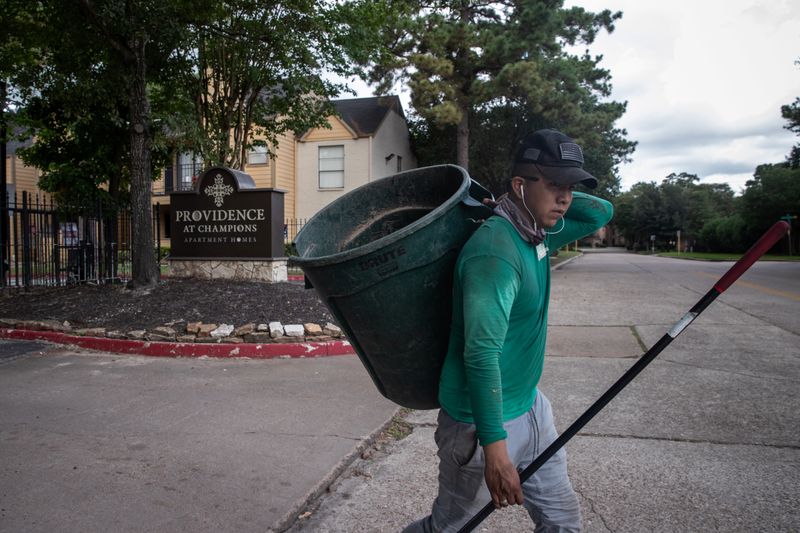
NEW YORK (Reuters) – Last month, as the coronavirus was surging in Houston, recently unemployed hospital secretary Ramzan Boudoin got more bad news: She had six days to vacate her apartment for failing to pay the rent.
A Texas ban on evictions had enabled Boudoin to keep the two-bedroom place she shared with her daughter and granddaughter while she searched for another job. But that moratorium expired on May 18. The landlord took legal action and Boudoin couldn’t come up with $2,997 plus interest to settle the judgment.
So this month Boudoin, 46, packed her family into a 2008 Nissan compact and headed to New Orleans, where she moved in with her mother and her sister’s family. In all, nine people share the packed three-bedroom house. Bedouin said her mother suffers from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, a lung illness that makes her particularly vulnerable to COVID-19 in a city where cases are rising at an alarming pace.
“Every minute, we are worried someone is going to give it to her,” Boudoin said.
As the coronavirus began to shut down large swaths of the U.S. economy in March, spiraling millions of Americans into unemployment, a patchwork of state and federal eviction bans were enacted to keep people in their homes. Now those protections are vanishing. Moratoriums have already expired in 29 states and are about to lapse in others. On Friday, a federal stay, which protects roughly one-third of American renters who live in buildings with mortgages backed by the federal government, will run out unless Congress acts fast.
As many as 28 million people could be evicted in coming months, according to Emily Benfer, a visiting law professor at Wake Forest University who is the co-creator of Princeton University’s Eviction Lab, a national research center on evictions. That’s nearly triple the estimated 10 million Americans who lost their homes during the years after the 2008 mortgage crisis.
Public health and housing experts say such a massive displacement of renters would be unprecedented in modern history. In addition to the hardship that comes with losing one’s home, they say, the evictions could lead to a second-wave public health crisis as the newly homeless are forced into shelters or tight quarters with relatives, increasing the risk of spread of COVID-19.
Evictions have resumed in cities including Houston, Cincinnati, Columbus, Kansas City, Cleveland and St. Louis, according to data compiled by Princeton University at its Eviction Lab. No single, comprehensive source exists to track U.S. evictions nationwide.
In Milwaukee, eviction filings dropped to nearly zero after Wisconsin instituted an emergency 60-day ban on evictions on March 27. But after that order was lifted May 26, evictions surged past their pre-pandemic levels. Milwaukee recorded 1,966 eviction filings in the seven weeks following the ban’s expiration, an 89% increase from 1,038 notices filed in the seven weeks leading up to the moratorium, the Princeton data show.
(For a graphic on Milwaukee evictions, see: https://tmsnrt.rs/2Bmc6Ae)
Dr. Nasia Safdar, an infectious disease physician and the medical director for infection prevention at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, said it’s impossible at this point to establish a scientific correlation between evictions and COVID-19 spread and deaths; diagnosed coronavirus cases are up 150% in Milwaukee, for example, since the eviction moratorium ended.
What is not in doubt among public health experts, she said, is that evictions are dangerous during a pandemic. “A key tenet of prevention in a pandemic is to have the infrastructure that will minimize transmission from person to person,” Safdar said. “Any activity that breaks down that structure … makes containment of a pandemic exceedingly difficult.”
A July 17 study from the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland found that in 44 U.S. cities and counties, eviction filings by landlords have almost returned to their usual levels in places where moratoriums have expired, or where bans were never enacted.
That study said evicted tenants are “at greater risk of contracting, spreading and suffering complications from COVID-19” because precariously housed people often are unable to shelter in place, and because they tend to use crowded emergency rooms for their primary medical care.
As evictions rise in some coronavirus hot spots, displaced families are doubling up with relatives or moving into shelters, creating conditions for the virus to spread widely, according to Diane Yentel, president of the Washington, D.C.-based National Low Income Housing Coalition, the U.S.’s premiere affordable housing policy group.
“In these cases where social distancing is difficult or impossible, the likelihood of them contracting and spreading coronavirus increases exponentially,” Yentel said.
A fragile safety net is adding to the strain. Enhanced $600 weekly unemployment benefits provided by the federal government are set to evaporate next week, at a time when the national unemployment rate is 13.3%.
Landlords say the pandemic is a crisis for them as well. Bob Pinnegar, CEO of the National Apartment Association, says eviction is always a “last resort,” but “the rental housing industry alone cannot bear the financial burden of the pandemic.”
He said nearly half the country’s landlords are mom-and pop operators who have invested in rental property for retirement income.
COVID POSITIVE, AND FACING EVICTION
For weeks, eviction courts across America were shuttered due to COVID-19. Now, over Zoom, conference calls and even in person in some places, proceedings are ramping up again.
In Houston’s Harris County, more than 5,100 eviction cases have been filed since the virus upended the U.S. economy in March, according to data compiled by Houston-based data science firm January Advisors.
That’s still roughly half of pre-pandemic levels. But it’s worrisome to public health advocates given that Harris County has seen confirmed coronavirus cases jump 500% since Texas’s eviction ban was lifted May 18, the Reuters COVID tracker shows.
Swapnil Agarwal is the 39-year-old founder of Nitya Capital, one of the largest landlords in Texas and owner of the Providence at Champions Apartment Homes from which Boudoin was evicted. During the pandemic, the company has filed more than 120 eviction notices against renters in Houston, a Reuters review of court records found. Houston-based Nitya has $2 billion in real estate assets under management, according to its website.
Agarwal said his firm evicted Boudoin because she was behind on her rent and “we realized that there was no intention to pay,” an allegation she disputes. He said Nitya has gone to great lengths to keep tenants in place and has provided $4 million in rent assistance to those who lost their jobs.
Meanwhile in Milwaukee, Mariah Smith was served an eviction notice on July 1. A shipping clerk for an aircraft parts maker, she lost her job in May. Smith said she hasn’t been able to pay her rent because she never received her $1,200 federal stimulus check and is still waiting to receive unemployment benefits.
Her fortunes have only gotten worse. Smith, 25, last week was diagnosed with coronavirus after experiencing chills, body aches and a sore throat. She said just walking leaves her winded.
On Thursday, she faces a court hearing on her eviction. Nick Homan, an attorney with the Legal Aid Society of Milwaukee, agreed to help. He said he’s handling around 25 eviction cases a week now, more than double his typical load.
After Reuters contacted Smith’s landlord — a limited liability company named LPT 46 — an attorney representing the firm, Marvin Bynum II, said the company just learned of Smith’s COVID diagnosis. “The landlord is hopeful that Ms. Smith recovers soon, and is confident the parties can swiftly reach a mutually amicable resolution,” Bynum said.
Homan said he’ll see what happens Thursday, but the larger issue remains.
“There’s nobody in any position of authority to stop eviction right now,” Homan said. “I don’t see anybody making decisions on public health. I only see landlords making decisions about their finances.”
(Reporting by Michelle Conlin; Editing by Tom Lasseter and Marla Dickerson)