(Reuters) – Fresh off an election in which former President Donald Trump made false claims of fraud, the U.S. Supreme Court is poised to ponder the legality of a restriction on early voting in Arizona that his fellow Republicans argued was needed to combat fraud.
The Republican-backed law, spurred in part by a video purportedly showing voter fraud that courts later deemed misleading, made it a crime to provide another person’s completed early ballot to election officials, with the exception of family members or caregivers.
Community activists sometimes engage in ballot collection to facilitate voting and increase voter turnout. Ballot collection is legal in most states, with varying limitations. Republican critics call the practice “ballot harvesting.”
Supreme Court arguments over the 2016 ban and another Arizona voting restriction – both ruled unlawful by a lower court – are scheduled for next Tuesday, with a decision due by the end of June. A broad ruling by high court, which has a 6-3 conservative majority, endorsing the restrictions could further weaken the Voting Rights Act, a landmark 1965 federal law that barred racial discrimination in voting, by making it harder to prove violations.
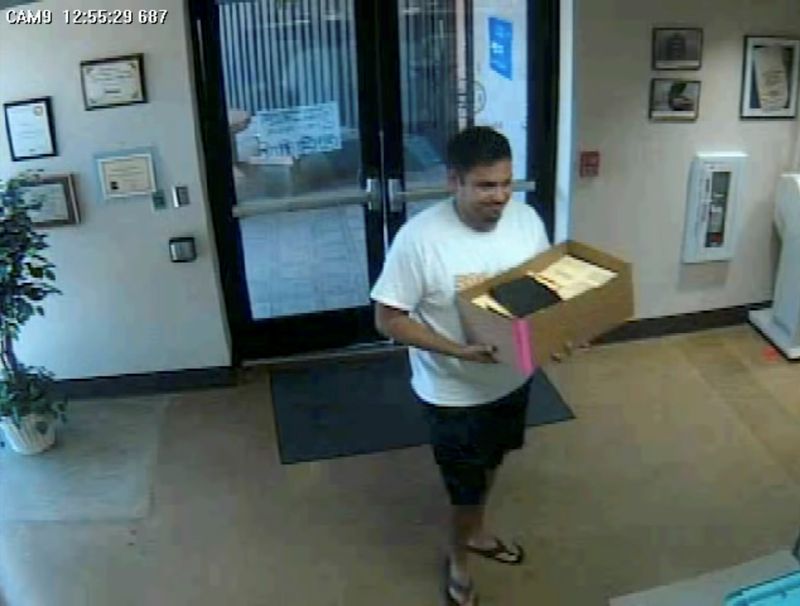
The video, taken from security camera footage, shows a man carrying a box of ballots into a Maricopa County Elections Department office. It was posted on a blog in 2014 by A.J. LaFaro, the Republican Party chairman at the time in Maricopa County, which includes Phoenix.
LaFaro’s post questioned whether the man was a U.S. citizen and called him a “violent thug” who was “stuffing the ballot box as I watched in amazement.” A judge later called the blog post “racially charged” and concluded that the footage showed no illegal activity. The man seen in the video filed an unsuccessful defamation suit against LaFaro.
Republican-governed states including Arizona have imposed a variety of voting restrictions in recent years. In the aftermath of Trump’s baseless claims of fraud, further curbs on voting are being pursued in 33 states following his Nov. 3 loss to Democrat Joe Biden in an election that drew record turnout, according to New York University School of Law’s Brennan Center for Justice.
‘THE MAIN TOOL’
At issue in the Supreme Court case is the Voting Rights Act’s Section 2, which bans any rule that results in voting discrimination “on account of race or color.” The court in 2013 gutted another section of the statute that determined which states with a history of racial discrimination needed federal approval to change voting laws.
Weakening Section 2 would eliminate “the main tool we have left now to protect voters against racial discrimination,” said Myrna Pérez, director of the Brennan Center’s Voting Rights and Elections Program.
“If there’s one thing that the election and the insurrection showed it’s that not everyone buys into the idea of free, fair and accessible elections,” Pérez added, referring to a pro-Trump mob’s Jan. 6 rampage at the U.S. Capitol.
The Supreme Court case also involves a longstanding Arizona policy that discards ballots cast in-person at a precinct other than the one to which a voter has been assigned. In some places, voters’ precincts are not the closest one to their home.
The case pits Arizona’s Republican Attorney General Mark Brnovich and the Arizona Republican Party against the Democratic National Committee and the Arizona Democratic Party, which sued over the restrictions. Arizona’s Democratic Secretary of State Katie Hobbs has backed the challenge.
The two sides differ sharply over whether genuine voter fraud must be documented to justify ballot restrictions.
“The notion that voter fraud must be proved in order to enact regulations of elections is not established in the law,” said Republican election lawyer Jason Torchinsky, who filed a brief backing Brnovich. “There are tons of areas where legislatures legislate without proving that some kind of fraud or crime has occurred.”
Jessica Ring Amunson, an attorney who represents Hobbs, said courts should take false fraud claims into account when evaluating the legality of voting restrictions.
Legislatures often justify such restrictions as necessary to tackle fraud and increase voter confidence, but “simultaneously they’re spreading baseless claims of voter fraud when none exists, and that is the very thing that is leading to people losing confidence in elections,” she added.
The San Francisco-based 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals last year found Arizona’s restrictions unlawful, though they remained in effect for the Nov. 3 election. It ruled that the restrictions disproportionately burdened Black, Hispanic and Native American voters and violated the Voting Rights Act.
The 9th Circuit also found that “false, race-based claims of ballot collection fraud” were used to convince Arizona legislators to enact that restriction with discriminatory intent, violating the U.S. Constitution’s prohibition on denying voting rights based on race.
U.S. District Judge Douglas Rayes in 2018 faulted Arizona’s legislature for its “misinformed belief that ballot collection fraud was occurring,” but upheld the voting restrictions. The 9th Circuit last year overturned that ruling.
(Reporting by Andrew Chung in New York; Editing by Will Dunham)