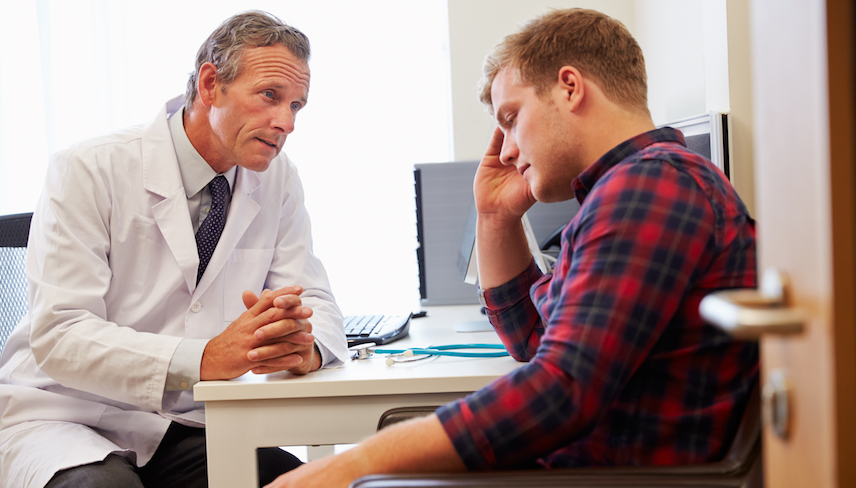
A pain in the balls. The feeling of constantly having to urinate, without relief. In some cases, erectile dysfunction. These are some of the symptoms of prostatitis, the most common urological ailment for men under 50 — and occurring in two out of three men over 50 years of age. The condition, which is inflammation of the prostate gland, varies in its severity, but it’s far from rare. According to the Prostatitis Foundation, fifty percent of men will experience symptoms in their lifetime. As June is Men’s Health Month, we spoke with urologist Dr. James Wysock, MD, assistant professor of Urology at NYU Langone, who explained what men need to know about the condition.
Prostatitis symptoms
Wysock says he treats patients for prostatitis fairly frequently. Especially among his younger patients, he says it’s one of the more common reasons men seek out a urological evaluation.
According to WebMD, there are four kinds of prostatitis. Acute bacterial prostatitis is an infection that occurs when bacteria spreads from the urinary tract to the prostate, while chronic bacterial prostatitis is a lingering, milder bacterial infection that can last for months. Chronic prostatitis, also known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, shares the symptoms of bacterial prostatitis, without bacteria present in tests. And finally, asymptomatic prostatitis, describes a condition in which a patient experiences prostate inflammation with no other symptoms.
Symptoms of prostatitis vary from mild to severe, temporary to chronic, explains Wysock. Increased urination coupled with a burning sensation, similar to a urinary tract infection (UTI), are common indicators. An inability to urinate, however, requires immediate attention. A dull pain in the scrotum and testicles is common, but anyone experiencing sharp, acute pain, especially if it’s located on one side, should seek immediate medical attention to rule out a testicular torsion. Fever and chills accompanying any of these symptoms could be a sign of an infection that requires a course of antibiotics.
In some cases, men will experience temporary erectile dysfunction. “If you have an inflammatory condition of the prostate, the nerves that control erections [which] are on the posterior aspect of the prostate, could be affected by the inflammation,” Wysock explains.
Prostatitis treatment
Treatment depends on evaluating the type of prostatitis and the presentation of symptoms.
The most common treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis, for example, is four-to-six weeks of antibiotics, says Wysock.
“You have to delve into possible causes,” he says. “Make sure men are emptying their bladder well, make sure there’s no anatomical cause, such as urinary retention or urethral stricture disease, stones in the bladder, etc.”
Some men might need a “urodynamic” to assess whether the bladder and urethra are functioning properly. Wysock says medication, such as Flomax, can help patients empty urine.
Wysock says chronic prostatitis can be difficult to treat, as it can lead to relapses of the symptoms over time and it’s hard to identify which bacteria is causing it.
As far as home remedies, Wysock recommends keeping well-hydrated, and taking NSAIDs like Ibuprofen to help reduce inflammation and offer pain relief
Prostatitis causes
There are several possibilities. An acute bacterial infection can be a cause. While stress could be a factor, there isn’t a direct link, Wysock says. It’s more like, “chronic prostatitis with recurrence can lead to a situation where it causes stress, which can lead to a cycle of increased stress leading to symptoms.”
It’s also important to rule out STDs, he says. Gonorrhea, chlamydia, or urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) can all lead to prostatitis-like symptoms. Again, it’s key to make sure there isn’t something more serious going on, such as a testicular torsion.